Introduction
Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) is one of the most significant concerns in the world of cybersecurity. APT attacks are sophisticated, targeted attacks aimed at infiltrating and extracting data from a target organization’s systems over an extended period. In this article, we will explore what APTs are, their impact on cybersecurity, and examine notable examples of APT attacks throughout history.
Learning Objectives
By reading this article, you will:
- Understand the concept of Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) and its key characteristics.
- Comprehend the impact of APTs on cybersecurity and the potential threats they pose.
- Discover notable APT attacks in history, how they were carried out, and their consequences.
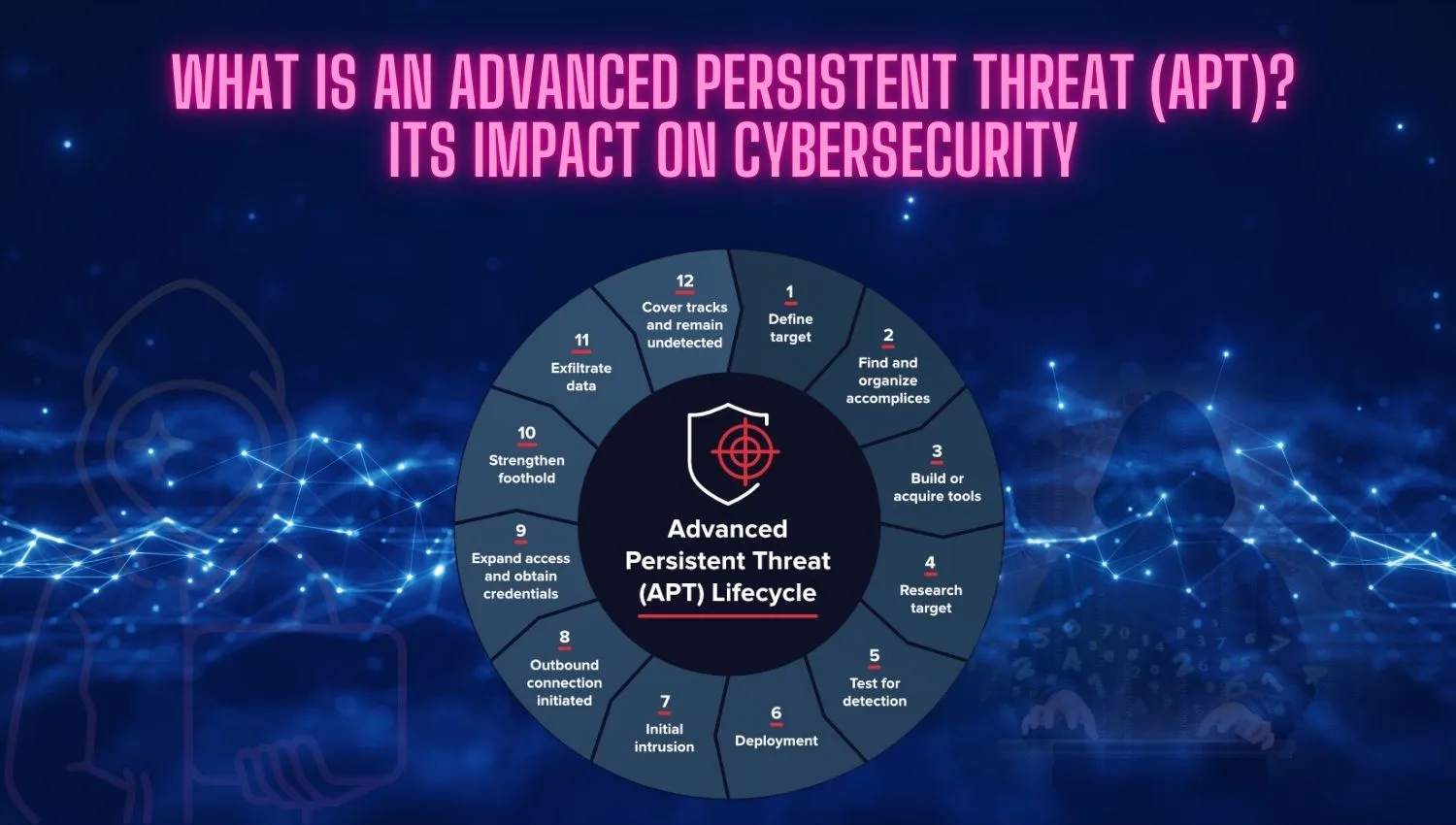
What is an Advanced Persistent Threat (APT)?
An Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) is a type of cyber attack that is long-term, sustained, and targeted towards a specific goal. APT attacks are typically carried out by highly skilled groups or state-sponsored actors seeking high-value data, sensitive information, or strategic objectives. These attacks use complex techniques to infiltrate systems and can remain undetected for extended periods, Cyber Threat Management: Security in the Digital World.
Key Characteristics of APTs:
- Sophistication: APT attacks use advanced techniques and tools to breach systems. Attackers employ zero-day vulnerabilities, social engineering, and other sophisticated methods to achieve their objectives.
- Persistence: Once successful, APTs can remain within the targeted system for an extended period. Attackers employ various techniques to remain undetected while exfiltrating data or maintaining a foothold in the system, APT and APT-GET in Linux Package Management Cheat Sheet.
- Targeted: APTs generally focus on specific organizations, sectors, or countries. These attacks aim to steal sensitive data or achieve strategic objectives related to the target’s value.
Cyber Security Specialist Coffee Mug
Black -Cyber Security Expert – Cyber Security Specialist Gift IT Network Engineer Computer Engineer Nerd
-10% $17.99 on AmazonImpact of APTs on Cybersecurity
APT attacks can cause significant and long-term damage to targeted organizations. These impacts include not only financial losses but also operational and reputational damage:
- Financial Losses: APTs can result in the theft of trade secrets, intellectual property, and sensitive customer data. Such data breaches can lead to substantial financial losses due to lost business, compensation claims, and other financial liabilities.
- Reputation Damage: The public disclosure of an APT attack can severely damage the target organization’s reputation. Customers and business partners may lose trust in the organization due to security failures.
- Operational Disruption: APTs can disrupt business operations and hinder the functioning of critical systems. This disruption can lead to decreased productivity and operational inefficiencies.
- Legal and Regulatory Consequences: Data breaches can lead to legal obligations and severe penalties. Target organizations may face lawsuits and regulatory actions due to violations of data protection laws.
Notable APT Examples
Concrete examples of APT attacks illustrate the severity and impact of these threats:
- Stuxnet (2010): Stuxnet was an APT attack targeting Iran’s nuclear program, causing damage to industrial control systems. This attack demonstrated the potential of cyber warfare by affecting physical systems and showcased the capabilities of cyber attacks in real-world scenarios.
- APT1 (2013): Linked to the Chinese People’s Liberation Army, APT1 conducted a cyber espionage campaign targeting various sectors in the United States, stealing trade secrets and sensitive information. This attack highlighted the global scale of cyber espionage activities.
- Operation Aurora (2009-2010): Operation Aurora was an APT attack against major technology companies like Google and Adobe, attributed to a group with ties to China. The attack led to the theft of significant amounts of user data and raised concerns about cybersecurity in major corporations.
- APT28 (Fancy Bear): Allegedly linked to Russia, APT28 conducted cyber espionage activities against NATO, the European Parliament, and the U.S. Democratic National Committee (DNC). The group gained notoriety for its activities during the 2016 U.S. Presidential Elections, Cybersecurity with Python: A Comprehensive Roadmap.
- Lazarus Group (2014): Associated with North Korea, the Lazarus Group executed a major cyber attack on Sony Pictures Entertainment, stealing and leaking company data. This attack demonstrated North Korea’s cyber capabilities and its impact on international relations.
Linux Basics for Hackers: Getting Started in Kali
This practical, tutorial-style book uses the Kali Linux distribution to teach Linux basics with a focus on how hackers would use them. Topics include Linux command line basics
-10% $19.36 on AmazonConclusion
Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) attacks represent one of the most significant challenges in modern cybersecurity. As high-targeted, sophisticated, and long-term threats, APTs can cause extensive damage to targeted organizations. Developing effective defense strategies against these attacks, continuously monitoring networks, and maintaining up-to-date security measures are crucial for modern cybersecurity. Notable historical APT attacks illustrate the seriousness and global impact of these threats. Organizations must build robust security strategies and be prepared to confront these advanced threats to protect their assets and data.



APT29 (Cozy Bear, The Dukes)
APT1 (Comment Crew) was horrible
I must admit that the Iranian attack has always remained in my mind as the biggest of them all.
This article provides a very clear and concise explanation of APTs, which is often a complex topic to grasp. Well done!”
“I loved the way the article breaks down the key characteristics of APTs. It’s very accessible, even for those new to cybersecurity.
How can small businesses protect themselves from APTs when they often don’t have the same resources as large corporations?
Small businesses can protect themselves by implementing strong cybersecurity policies, investing in threat detection tools, and regularly updating their systems.
Partnering with a managed security service provider (MSSP) can also offer additional layers of defense
Are there any early warning signs that organizations can look out for to detect APTs before too much damage is done?
Early warning signs of APTs often include unusual network traffic, abnormal user activity, and unauthorized access attempts. Regular monitoring and threat intelligence tools can help detect these anomalies
Many APT groups use zero-day vulnerabilities—flaws that are unknown to software vendors—to gain access to systems. These vulnerabilities remain unpatched, allowing attackers to exploit them for extended periods.
APT attacks often exploit insider threats, where employees unknowingly assist attackers by clicking on malicious links or providing access to sensitive systems. Internal awareness and training programs are crucial in preventing these vulnerabilities.