Introduction
In today’s digital landscape, understanding the vulnerabilities of internet-connected devices is crucial for cybersecurity. Shodan has emerged as a unique tool in this domain, often referred to as “the search engine for hackers.” Developed by John Matherly in 2009, Shodan allows users to discover various devices connected to the internet, providing insights that can be invaluable for both security professionals and malicious actors alike. This tutorial aims to introduce you to Shodan search engine for cybersecurity, its functionalities, and how to effectively utilize it for security assessments.
Learning Objectives
By the end of this tutorial, you will be able to:
- Understand the role and significance of Shodan in cybersecurity.
- Perform basic and advanced searches using Shodan.
- Identify vulnerabilities in internet-connected devices.
- Utilize Shodan responsibly and ethically.
Shodan: A Search Engine for Hackers
Shodan operates differently from traditional search engines like Google. While Google indexes web pages, Shodan scans the internet for devices and collects metadata known as “banners.” These banners contain information about the device type, software version, and open ports. Users can leverage this data to perform reconnaissance on their own systems or identify vulnerable devices that could be exploited. Shodan’s capabilities make it a powerful tool for penetration testers and IT professionals. It helps in identifying exposed devices that may not be adequately secured, allowing organizations to take proactive measures against potential threats. The Shodan search engine for cybersecurity provides unparalleled visibility into the ecosystem of connected devices.
Basic Search Examples
To get started with Shodan, here are some basic search queries you can use:
Webcam Search:
To find all webcams connected to the internet:
webcam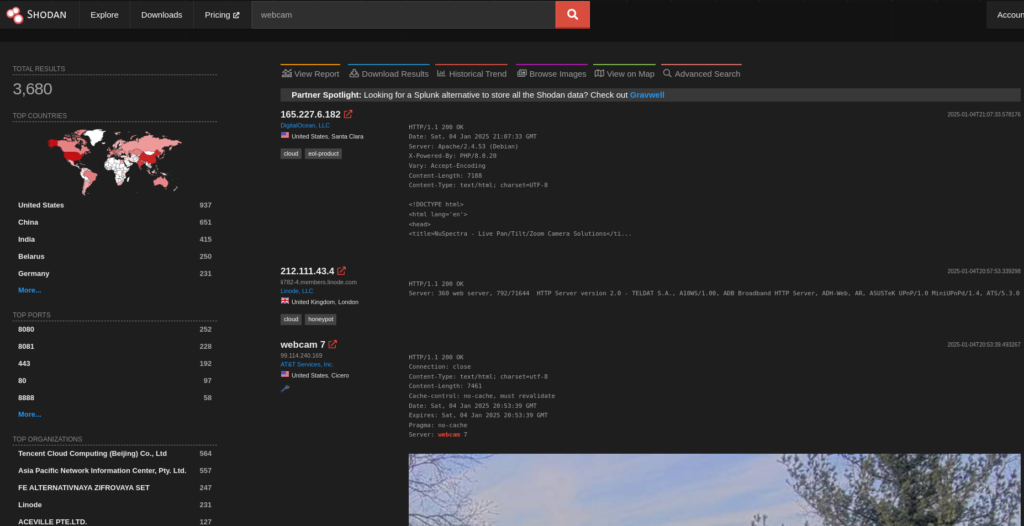
Traffic Signals:
To locate traffic signal control systems:
traffic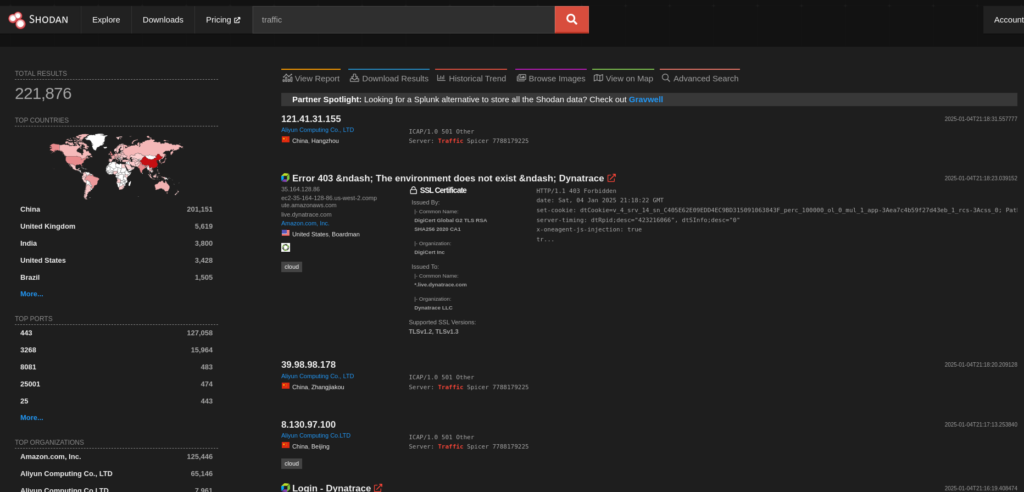
Unsecured Devices:
To find devices that are publicly accessible without password protection:
default password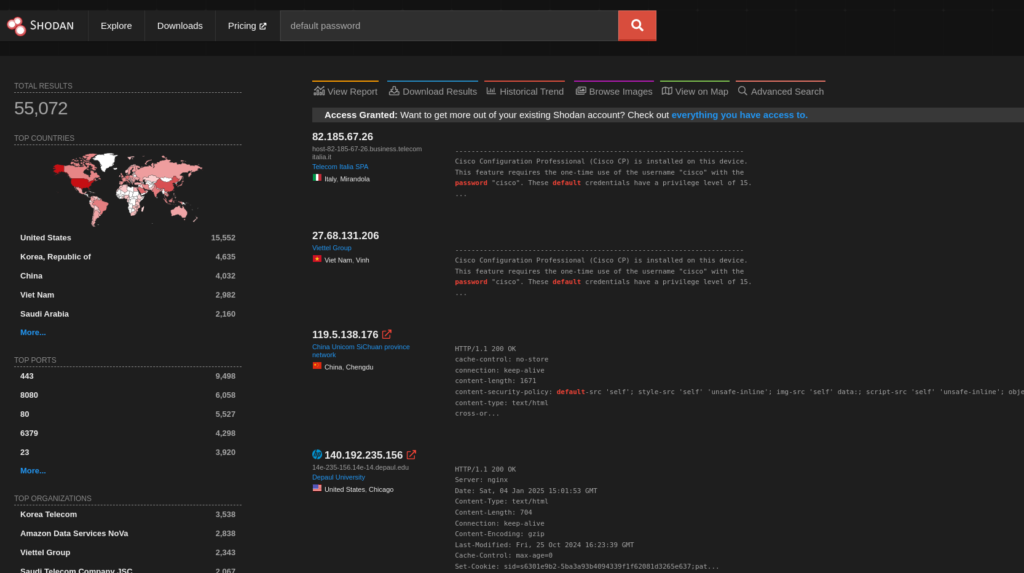
These searches provide a glimpse into the types of devices that can be discovered using Shodan.
Using Advanced Search Operators
Shodan also offers advanced search operators that allow for more refined searches. Here are some examples to enhance your Shodan search engine for cybersecurity experiences:
Device Type Filtering:
To find specific types of devices:
product:"Apache"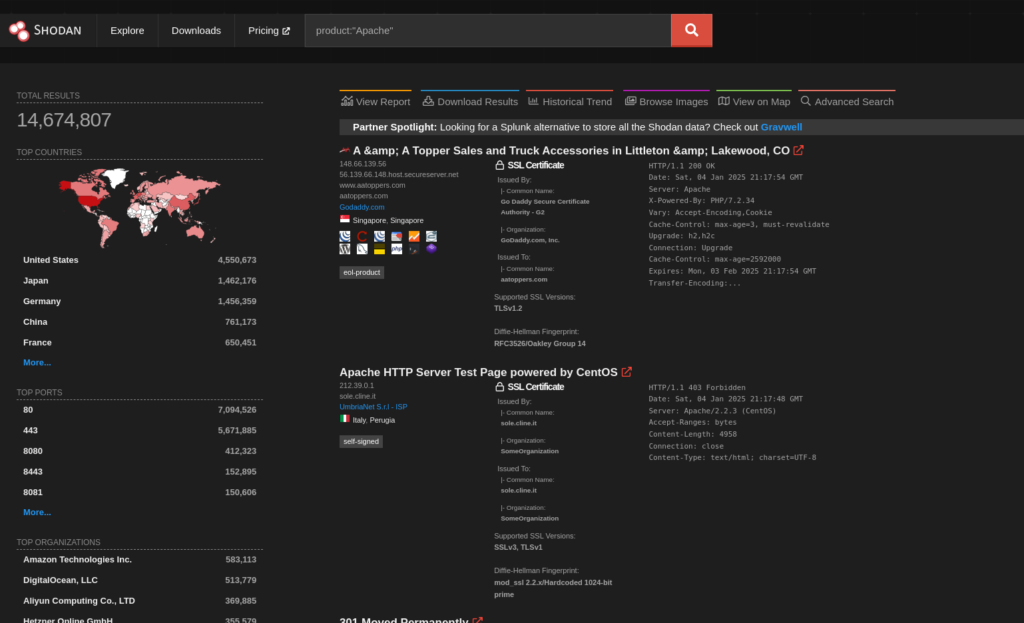
Location-Based Searches:
To find devices in a specific country or city:
country:"US" city:"New York"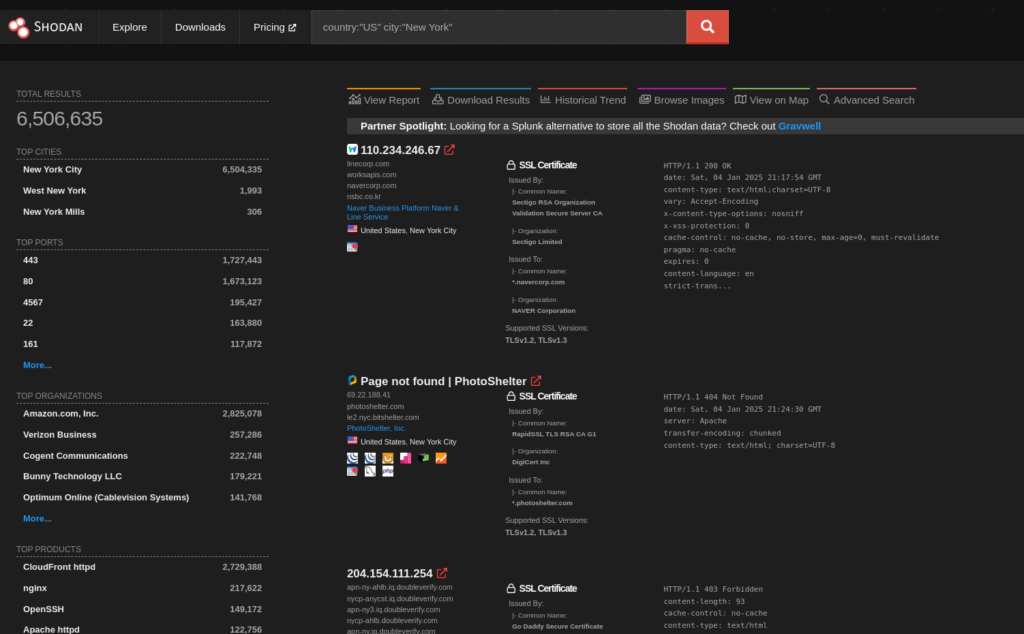
Open Port Searches:
To identify devices with specific open ports:
port:22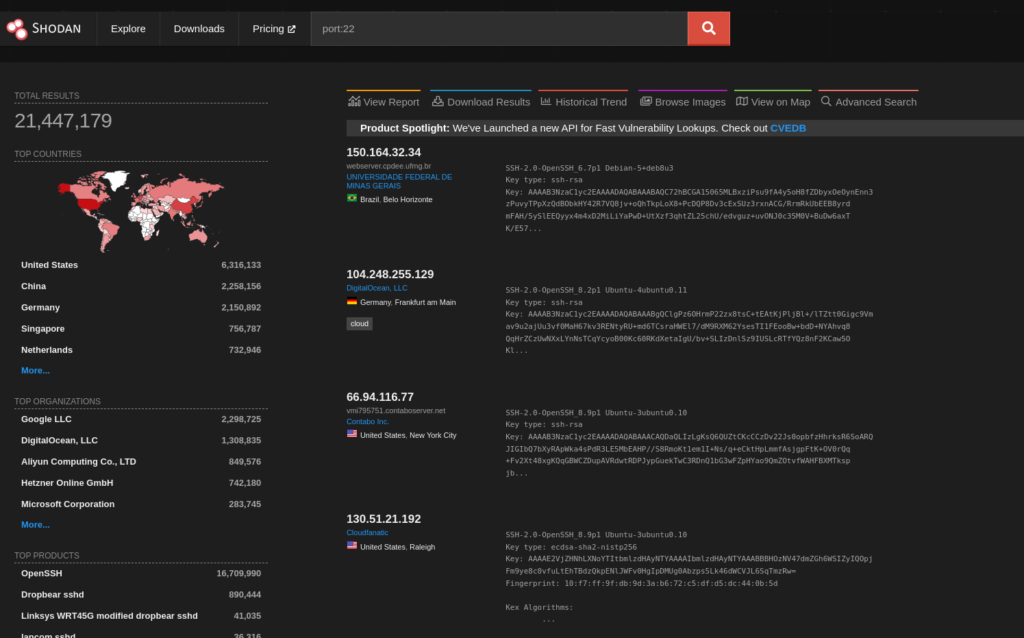
Combining Filters:
For more complex queries, you can combine multiple filters:
nginx country:"EG" port:80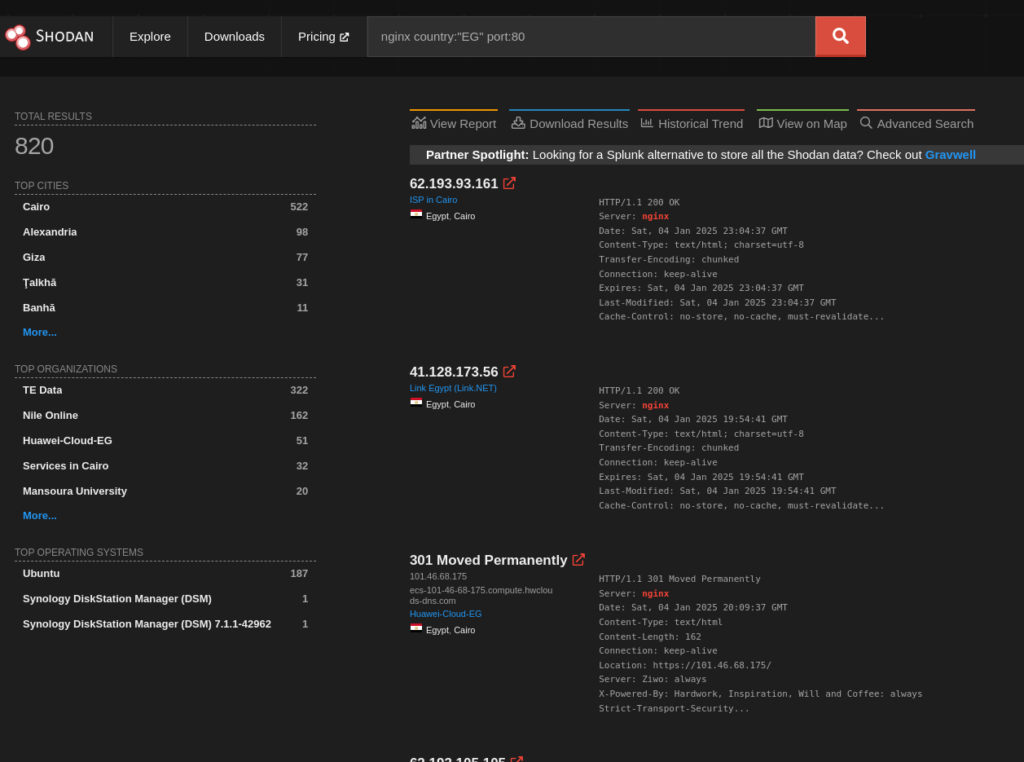
vuln:”[CVE-ID]”:
Finds devices affected by a specific Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) ID. Perform this advanced search to strengthen the Shodan search engine for cybersecurity tasks.
vuln:"CVE-2021-26855"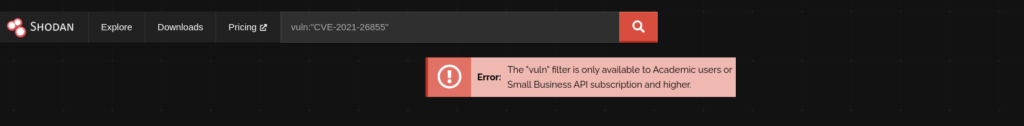
These advanced operators enhance your ability to pinpoint specific vulnerabilities and device types.
Shodan Dork Cheat Sheet
For those looking to maximize their effectiveness with Shodan, utilizing a dork cheat sheet can be incredibly helpful. A dork cheat sheet provides a collection of predefined search queries that can help users quickly find specific types of data or vulnerabilities. For a comprehensive list of dorks tailored for Shodan, refer to the Shodan Dork Cheat Sheet.
Conclusion
Shodan is an invaluable resource in the realm of cybersecurity, offering insights into the vast network of internet-connected devices. By understanding how to effectively use Shodan, security professionals can identify vulnerabilities within their networks and take appropriate action to secure their systems. However, it is essential to use this powerful tool responsibly and ethically. With the knowledge gained from this tutorial on the Shodan search engine for cybersecurity, you are now better equipped to explore Shodan and enhance your cybersecurity posture.
You May Be Interested In:


