Introduction
In today’s digital landscape, cybersecurity has become a critical concern for individuals and organizations alike. With the increasing use of web applications, cyberattacks targeting these platforms have also proliferated. Among the various types of attacks, brute force attacks are one of the simplest and most effective methods. In this article, we will explore how to conduct a brute force attack on a web application’s login page using Burp Suite. Burp Suite is a widely used tool for testing the security of web applications, and understanding these attack methods is essential for developing effective defense mechanisms.
Learning Objectives
By reading this article, you will gain knowledge about the following topics:
- The fundamental concepts of brute force attacks and how they work.
- The features and usage of Burp Suite.
- The step-by-step process for executing a brute force attack.
- How to evaluate and analyze the results of the attack.
- Ethical hacking principles and legal responsibilities.
Brute Force Attack with Burp Suite
Burp Suite provides a comprehensive set of tools for testing web applications. It can be effectively used to automate the process of testing various username and password combinations. In this process, we will conduct a brute force attack on the login page of a target web application to identify potential security vulnerabilities. Brute force attacks typically involve automated tools that attempt to guess usernames and passwords by systematically trying all possible combinations. These attacks are particularly effective against weak passwords or default login credentials.
Let’s Begin with the Attack Steps
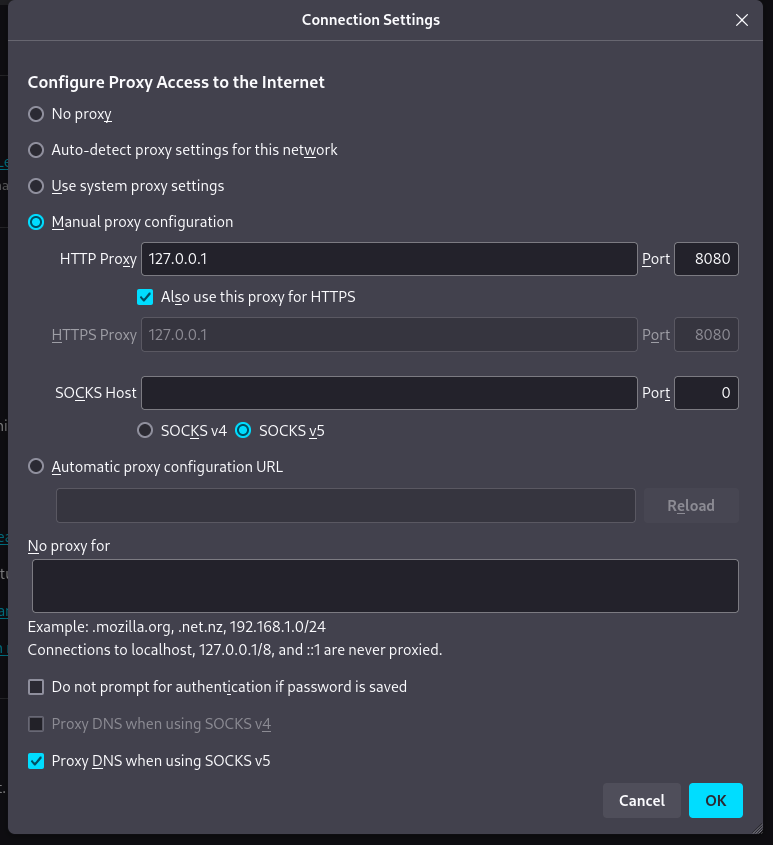
1. Configure Proxy Settings:
Navigate to the “Proxy” tab in Burp Suite and go to the “Options” section to configure proxy settings. Set up a proxy listener (usually on 127.0.0.1:8080) that will capture your browser’s traffic.
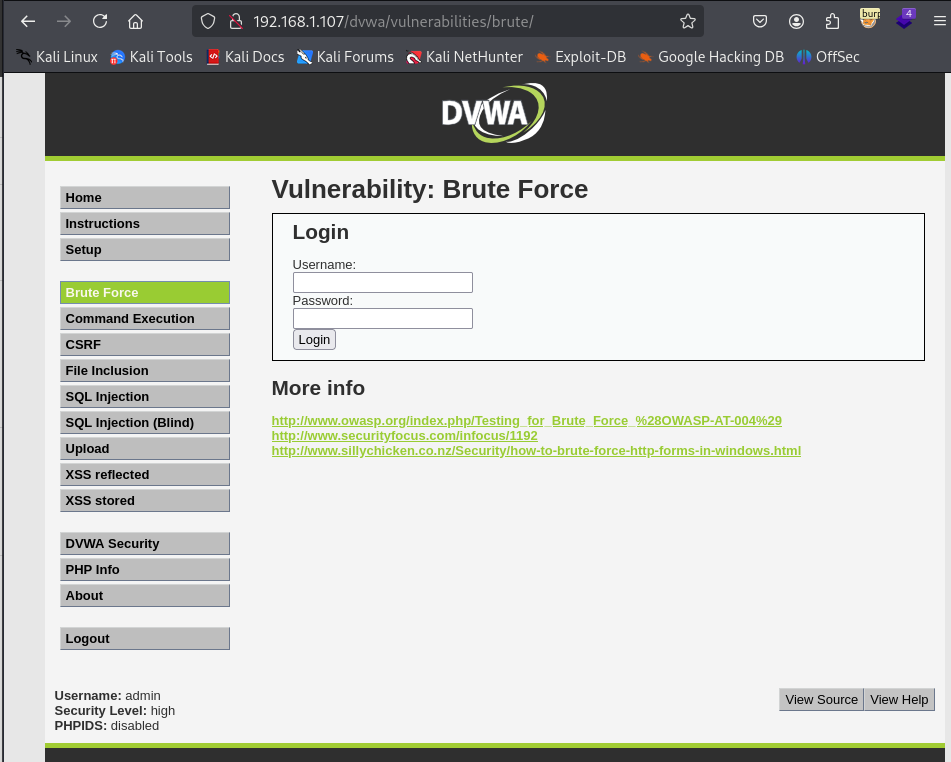
2. Set Up Target Web Application:
Identify the URL of your target web application and open it in your browser. Ensure that your browser is configured to route traffic through Burp Suite’s proxy settings.
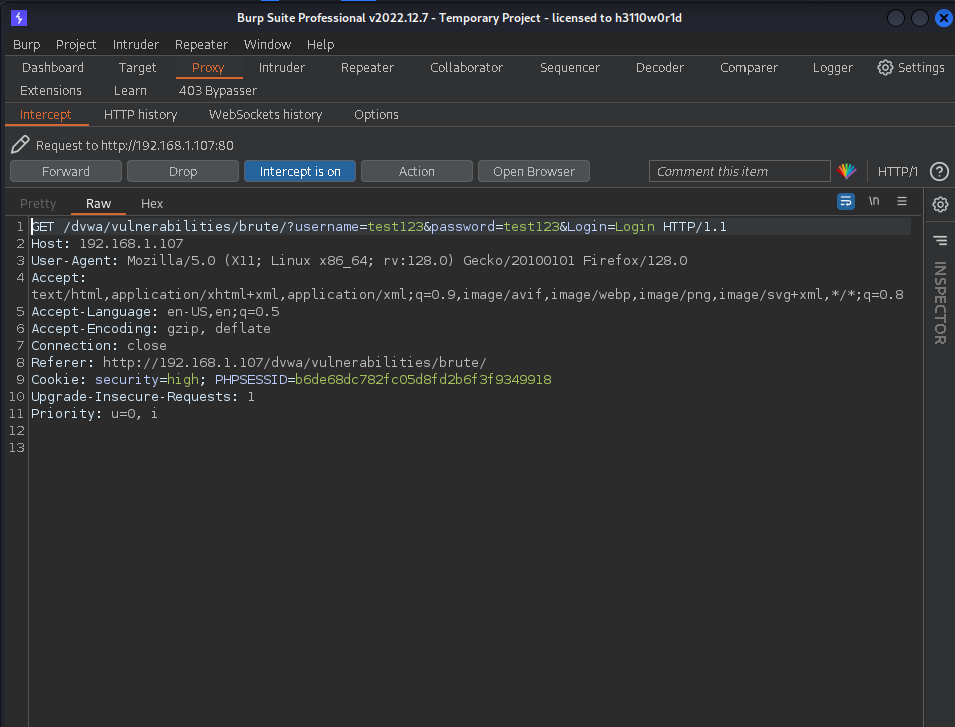
3. Capture the Login Request:
Fill in the login form in your browser (entering a username and password) and attempt to log in. During this process, Burp Suite will intercept the request being sent to the server.
4. Send Request to Intruder:
Right-click on the captured request and select “Send to Intruder” to forward it to the Intruder tool within Burp Suite.
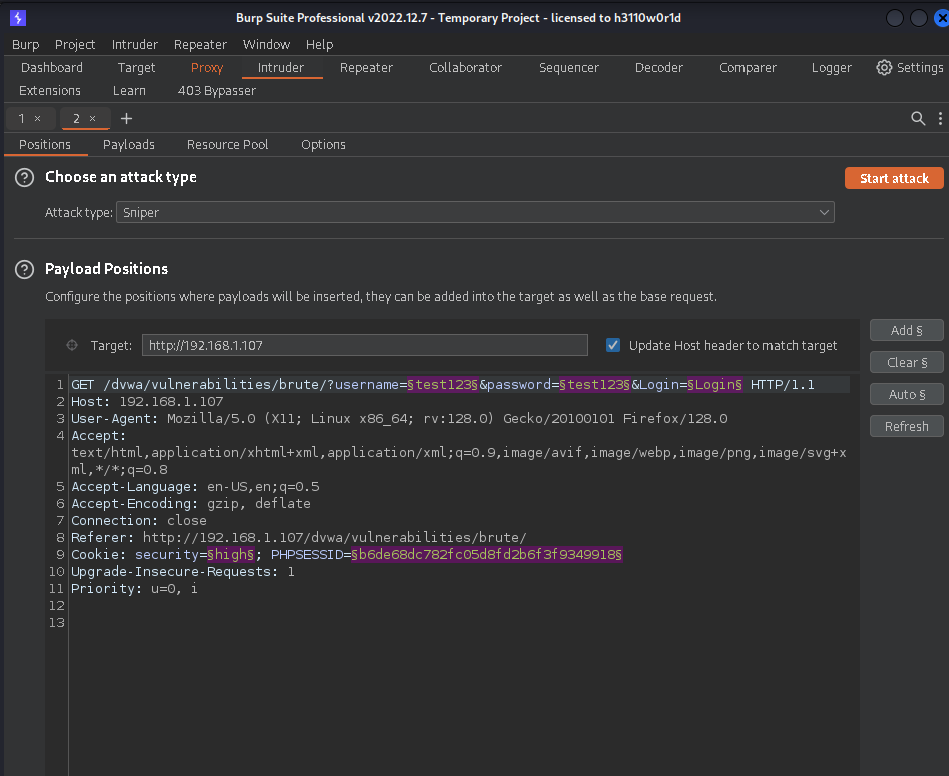
5. Define Positions:
Switch to the Intruder tab and go to the “Positions” section. Here, you will specify which parts of the request you want to target for brute force attacks—typically, this will be the password field (and optionally, the username field).
6. Load Wordlist:
Upload a wordlist that contains potential usernames and passwords for testing. This list should include combinations that you want to try against the target application. Wordlists can often be found online or created manually.
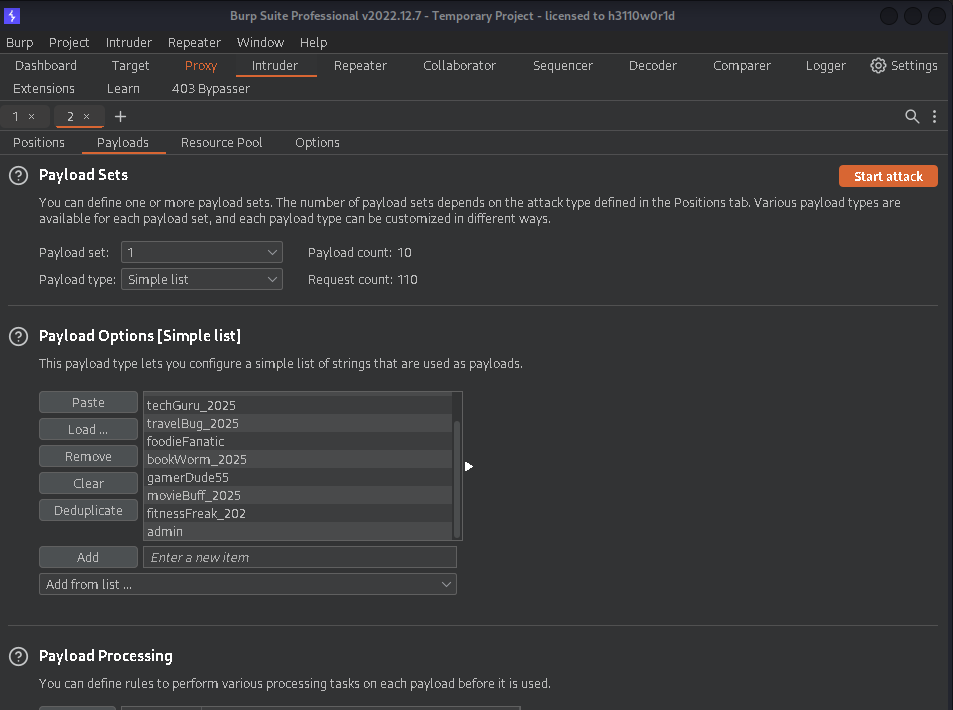
7. Start the Attack:
After configuring all settings, click on “Start Attack” to initiate the brute force attack. The Intruder tool will automatically send requests using each combination from your wordlist against the target application.
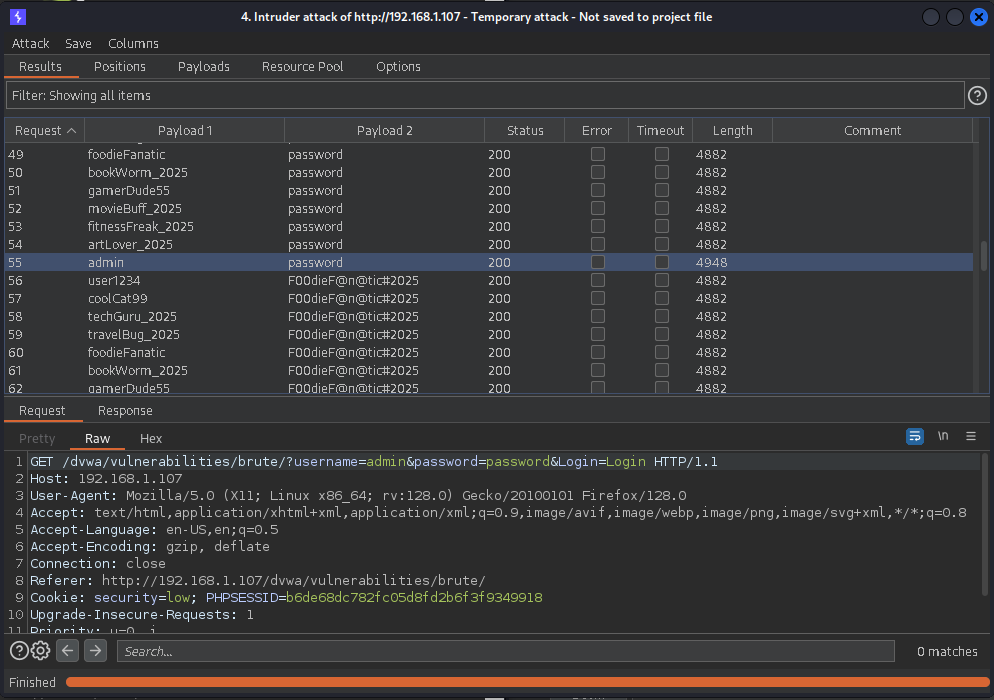
8. Monitor Results:
During the attack, Burp Suite will display results in real-time. Pay attention to response codes (like 200 or 403) as successful login attempts typically return different response codes compared to failed attempts.
Conclusion
In this article, we have detailed how to conduct a brute force attack on a web application’s login page using Burp Suite. Brute force attacks can be effective against weak passwords or default credentials; however, robust password policies and security measures can mitigate these risks. It is crucial to remember that ethical hacking and security testing should only be conducted in authorized environments; otherwise, you may face legal repercussions. Continuous learning is essential in cybersecurity—staying informed about new threats and defense strategies helps both individuals and organizations better understand their vulnerabilities while becoming more resilient against cyber threats.


In the Professional version of Burp Suite, you can perform brute force very fast, but the Community Edition version is very slow.
yes, that’s why alternative methods are used
Could you please tell me about these methods?
for example: wfuzz
check out here: Web Application Security Testing with Wfuzz