Introduction
In today’s digital era, companies of all sizes and industries rely heavily on interconnected systems, cloud-based platforms, and digital communication tools to manage their operations and serve their customers. This deep integration of technology has brought about significant opportunities for innovation, efficiency, and business growth. However, it has also introduced a host of new vulnerabilities and cyber risks. Organizations now face a rapidly evolving threat landscape, with dangers ranging from data breaches and ransomware attacks to insider threats and sophisticated phishing schemes. As these risks become more prevalent and complex, ensuring robust network security is no longer just a technical concern-it is a fundamental necessity for maintaining business continuity, protecting sensitive data, and preserving the trust of customers and partners.
Learning Objectives
- Understand why network security is crucial for modern businesses.
- Learn about the key threats facing corporate networks.
- Explore best practices and strategies for implementing strong network security.
- Recognize the role of employee awareness and organizational policies in safeguarding digital assets.
Why Should Companies Ensure Network Security?
The ongoing digital transformation of business processes has fundamentally altered the way organizations operate, communicate, and deliver value. As a result, there has been an exponential increase in both the volume and the strategic importance of data stored, processed, and transmitted across corporate networks. This data often includes highly sensitive information such as customer records, intellectual property, trade secrets, financial transactions, and confidential communications-all of which are prime targets for cybercriminals and malicious actors. A single security breach can have far-reaching and long-lasting consequences for a company. Financial losses may arise not only from direct theft or fraud but also from operational downtime, regulatory fines, and the costs associated with investigating and remediating the incident. Legal liabilities can emerge if the breach involves the exposure of personal or regulated data, potentially resulting in lawsuits or penalties under frameworks such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and other industry-specific regulations. Perhaps most damaging of all is the erosion of customer trust and brand reputation, which can take years to rebuild after a publicized security incident.
Moreover, the regulatory environment is becoming increasingly stringent, with governments and industry bodies around the world imposing strict requirements on how companies must protect and manage data. Compliance with these regulations is not optional; failure to adhere can result in severe sanctions and loss of business opportunities. For all these reasons, network security is not simply a matter of technical best practice-it is a core business imperative and a legal obligation that cannot be ignored.
The Importance of Network Security for Businesses
Network security is the bedrock upon which the entire digital infrastructure of a modern company is built. It is responsible for ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the information and services that drive business success. Without effective network security, companies are left vulnerable to a wide array of threats that can disrupt operations, compromise sensitive data, and undermine stakeholder confidence.
- Prevents Unauthorized Access: By establishing robust access controls and authentication mechanisms, network security ensures that only authorized individuals and devices can interact with critical systems and information. This reduces the risk of data leaks, sabotage, and other forms of unauthorized activity that could harm the organization.
- Safeguards Sensitive Data: Through the use of encryption, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and secure authentication protocols, network security protects valuable business information from theft, tampering, or loss. This is especially important for organizations that handle large volumes of personal or proprietary data.
- Maintains Business Continuity: Cyberattacks, hardware failures, and other disruptions can bring business operations to a standstill. Strong network security measures help defend against these incidents, ensuring that essential services remain available and that the company can recover quickly in the event of a disruption.
- Builds Customer Trust: In an age where data breaches are widely publicized and customer awareness of privacy issues is high, demonstrating a commitment to security is essential for maintaining and growing business relationships. Clients and partners are more likely to engage with companies that can prove their data is safe.
- Supports Compliance: Adhering to recognized security standards and best practices helps companies meet the requirements of regulatory frameworks, reducing the risk of fines, sanctions, and legal disputes. Compliance also enhances the company’s reputation and can be a key differentiator in competitive markets.
How Should Companies Ensure Network Security?
To effectively secure their networks, companies must adopt a holistic, multi-layered approach that combines technology, processes, and people. Key strategies include:
Basic Network Security Measures
- Physical Security: Physical security is the first line of defense in network protection. Companies must ensure that all network devices, such as servers, routers, switches, and other critical infrastructure components, are housed in secure environments. This means implementing access controls to server rooms, using biometric authentication systems or access cards, installing surveillance cameras, and ensuring that only authorized personnel can physically interact with these devices. Such precautions minimize the risk of tampering, theft, or sabotage that could compromise the entire network.
- Firewall Implementation: Firewalls act as a protective barrier between the company’s internal network and external networks, such as the internet. By filtering incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules, firewalls help block unauthorized access and prevent malicious traffic from entering the network. Companies should deploy both hardware and software firewalls and regularly update their configuration to adapt to emerging threats and changing business requirements.
- VPN (Virtual Private Networks): With the rise of remote work and geographically distributed teams, secure remote access has become more important than ever. By implementing VPN technologies, companies can ensure that data transmitted between remote users and the corporate network is encrypted and protected from interception. VPNs also help authenticate users and devices, reducing the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive company resources.
- Antivirus and Antimalware Solutions: The threat landscape is filled with various forms of malicious software, including viruses, worms, ransomware, and spyware. To defend against these threats, it is essential for companies to deploy reputable antivirus and antimalware solutions across all endpoints and servers. These tools should be configured to perform real-time scanning, automatic updates, and regular full-system scans to detect and neutralize threats before they can cause harm.
- Access Control and Identity Management: Limiting access to sensitive information and critical systems is a cornerstone of network security. Companies should implement robust access control policies that adhere to the principle of least privilege, ensuring that users and devices have access only to the resources necessary for their roles. Identity management solutions, such as centralized directories and single sign-on (SSO) systems, can help streamline user authentication and simplify the management of access rights, while regular reviews of permissions help prevent privilege creep.
- Strong Password Policies and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Weak or reused passwords are a common entry point for attackers. To mitigate this risk, companies should enforce strong password policies that require complex, unique passwords and mandate regular password changes. Additionally, implementing multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more forms of verification before gaining access to sensitive systems or data.
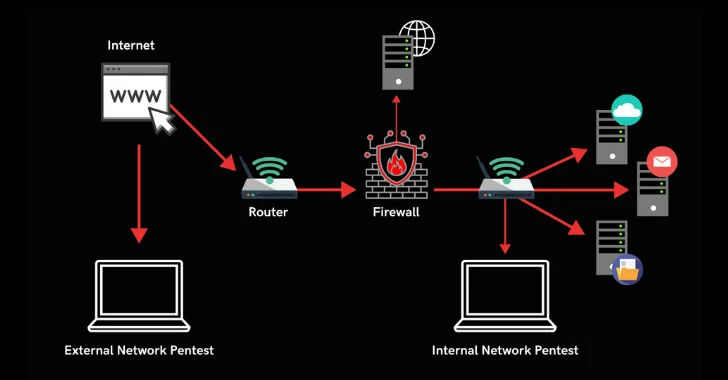
Advanced and Routine Controls
- Penetration Testing: Regular penetration testing is a proactive approach to identifying vulnerabilities within the company’s network infrastructure, applications, and security controls. By simulating real-world cyberattacks, penetration testers can uncover weaknesses that may not be apparent through routine monitoring. The results of these tests enable companies to address security gaps before they can be exploited by malicious actors.
- Network Traffic Analysis and Continuous Monitoring: Monitoring network traffic in real time is essential for detecting suspicious activities, such as unusual data transfers, unauthorized access attempts, or malware communication. Companies should deploy Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS) to analyze network packets and alert administrators to potential threats. Continuous monitoring not only helps in early detection but also supports rapid response to incidents, minimizing potential damage.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): SIEM solutions aggregate and analyze logs and security events from across the organization’s IT environment. By correlating data from multiple sources, SIEM platforms can identify patterns indicative of cyberattacks or policy violations. Automated alerts and dashboards provide security teams with actionable insights, enabling them to respond quickly and efficiently to emerging threats.
- Regular Software and Hardware Updates: Cybercriminals often exploit known vulnerabilities in outdated software and hardware. To counter this risk, companies must establish processes for regularly updating operating systems, applications, firmware, and network devices. Patch management tools can automate the deployment of updates, ensuring that all systems remain protected against the latest threats.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Data loss can result from cyberattacks, hardware failures, or human error. To ensure business continuity, companies should implement comprehensive backup strategies that include regular, automated backups of critical data. Backups should be encrypted, stored securely (ideally offsite or in the cloud), and tested periodically to verify their integrity and the effectiveness of recovery procedures.
Employee Training and Awareness
- Social Engineering and Phishing Awareness: Human error remains one of the weakest links in network security. Attackers frequently use social engineering tactics, such as phishing emails, to trick employees into revealing sensitive information or downloading malware. Regular training sessions should educate employees about the latest cyber threats, teach them how to recognize suspicious activity, and reinforce the importance of following security best practices in their daily work.
- Security Policies and Procedures: Clearly defined and well-communicated security policies form the foundation of a secure organization. Companies should develop comprehensive information security policies that outline acceptable use, data handling, incident response, and other critical areas. These policies should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changes in technology, business processes, and the threat landscape, and all employees should be required to acknowledge and adhere to them.
Wireless Network Security
- Strong Encryption (WPA3): Wireless networks are particularly vulnerable to eavesdropping and unauthorized access. To mitigate these risks, companies should use the latest encryption standards, such as WPA3, for all wireless access points. Default passwords must be changed immediately upon installation, and network names (SSIDs) should be hidden when possible to make it harder for attackers to identify and target the network.
- MAC Address Filtering: By implementing MAC address filtering, companies can restrict wireless network access to only authorized devices. While this measure is not foolproof, it adds an additional layer of control and can deter casual attempts to connect to the network.
Legal Compliance and Log Management
- Comprehensive Log Management: Maintaining detailed logs of network activity is essential for both security and regulatory compliance. Companies should collect and securely store logs from firewalls, servers, applications, and other critical systems. These logs provide valuable forensic evidence in the event of a security incident and support compliance with industry regulations and legal requirements. Regular log reviews and automated analysis tools can help identify anomalies and ensure that potential threats do not go unnoticed.
By implementing these comprehensive and continuous measures, companies can build a resilient network security posture that not only protects their digital assets from a wide range of cyber threats but also fosters trust among customers, partners, and stakeholders. Investing in network security is not a one-time effort but an ongoing process that must evolve alongside technological advancements and the ever-changing threat landscape.
Conclusion
As the digital landscape continues to evolve at a rapid pace, the necessity for companies to prioritize network security has never been greater. Cyber threats are not only becoming more frequent but also more sophisticated, leveraging advanced techniques to bypass traditional defenses and exploit human and technical vulnerabilities. The potential consequences of a security breach-ranging from financial losses and legal penalties to reputational damage and loss of customer trust-are more severe than ever before. To effectively address these challenges, companies must move beyond basic security measures and adopt a comprehensive, proactive approach that integrates advanced technologies, robust processes, and a pervasive culture of security awareness throughout the organization. This means investing in the latest security solutions, regularly assessing and updating security practices, and ensuring that every employee understands their role in protecting the company’s digital assets.
Ultimately, network security is not just an IT concern or a box to be checked for compliance purposes. It is a strategic imperative that underpins the long-term success and sustainability of any business operating in today’s interconnected world. By making network security a top priority, companies can protect their assets, maintain business continuity, and build lasting trust with customers, partners, and stakeholders.
You May Be Interested In:
External sources:
- Small Business Network Security Checklist – Cisco
- You need to ensure your company’s network is secure
Contact Us for Network Security

If you want to strengthen your company’s network security or need expert guidance tailored to your business needs, we are here to help. For professional support, consulting, or customized cybersecurity solutions, feel free to reach out to us.
For detailed information about our services, to request a custom quote, or to get in touch directly, please visit our Contact Information page.
You can also reach us via email at:
halildeniz313@gmail.com
or more detail with:
Network Security Services
Take the next step in securing your network security contact us today for professional and reliable network security support.

