Introduction
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a fundamental component of the internet, translating human-readable domain names into IP addresses that computers use to access websites. This critical infrastructure serves as the backbone of internet navigation, allowing users to connect to resources without needing to remember complex numerical addresses. However, the DNS is not inherently secure and is vulnerable to various cyber threats, making DNS security essential for protecting online resources. DNS security involves safeguarding the DNS infrastructure from attacks, ensuring that users are directed to legitimate websites, and preventing unauthorized access or data manipulation.
Learning Objectives
This article aims to provide insights into:
- The concept of DNS security and its significance in today’s digital landscape.
- The role of Domain Name System Security Extensions (DNSSEC) in enhancing DNS security.
- Tools and techniques available for implementing effective DNS security measures.
Why is DNS Security Important?
DNS security is crucial for several reasons:
- Protection Against Cyber Attacks: Cybercriminals can exploit vulnerabilities in the DNS system to redirect users to spoofed websites, leading to data theft or malware infections. For instance, attackers may use techniques like DNS hijacking or cache poisoning to manipulate DNS responses. By securing the DNS infrastructure, organizations can mitigate these risks and protect sensitive information from falling into the wrong hands.
- Data Integrity: Ensuring the integrity of DNS records is vital for maintaining trust in online communications. With threats like DNS spoofing and cache poisoning, attackers can manipulate DNS responses, leading users to malicious sites that appear legitimate. Implementing robust define security measures helps maintain the authenticity of data transmitted over the internet, ensuring that users receive accurate information.
- User Trust: A secure DNS environment fosters user confidence. When users know that their connections are protected from potential threats, they are more likely to engage with online services without fear of fraud or phishing attacks. Trust is a critical factor in online interactions; therefore, maintaining a secure DNS infrastructure is essential for businesses that rely on digital transactions.
- Improved Performance: Secure DNS servers can offer faster lookup times and improved connection speeds, enhancing overall user experience and productivity. This efficiency is particularly important for businesses that rely on web-based applications and services. By reducing latency and ensuring reliable access to resources, organizations can improve their operational efficiency.
- Prevention of Service Disruptions: Cyber attacks targeting the DNS can lead to significant service disruptions. For example, Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks can overwhelm DNS servers with excessive traffic, making it difficult for legitimate users to access websites. By implementing effective DNS security measures, organizations can minimize the risk of such disruptions and maintain continuous service availability.
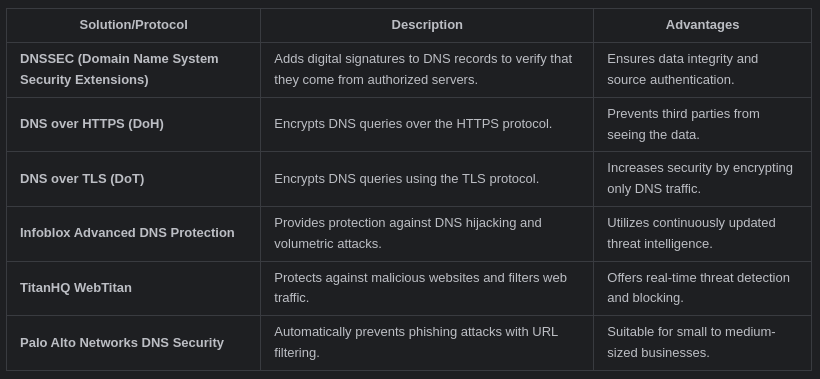
Tools for Enhancing DNS Security
Several tools are available to bolster DNS security, including:
1. dnsrecon
A powerful tool for discovering DNS records and performing enumeration.
dnsrecon -d example.com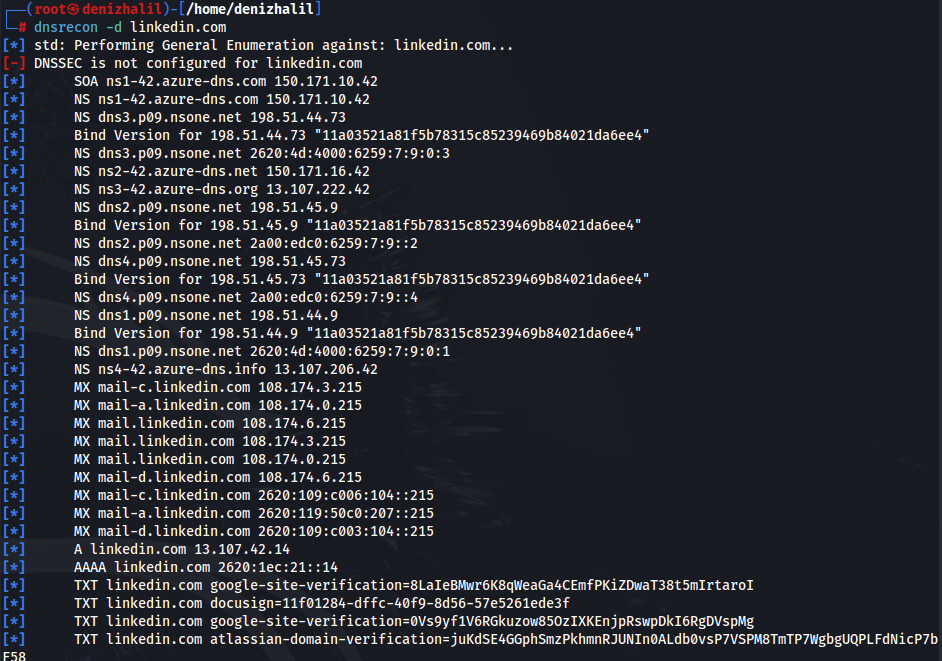
This command queries the DNS records for “example.com,” providing valuable insights into the domain’s configuration.
2. dig
A command-line utility for querying DNS information.
dig example.com ANY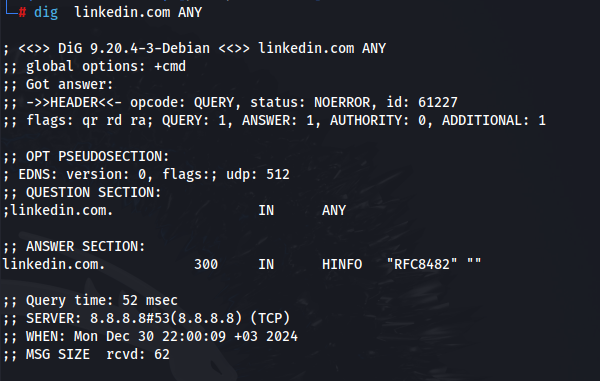
This command retrieves all available DNS records for “example.com,” helping administrators understand the domain’s setup.
3. The Harvester
An information-gathering tool that collects data about a target domain.
theHarvester -d example.com -b duckduckgo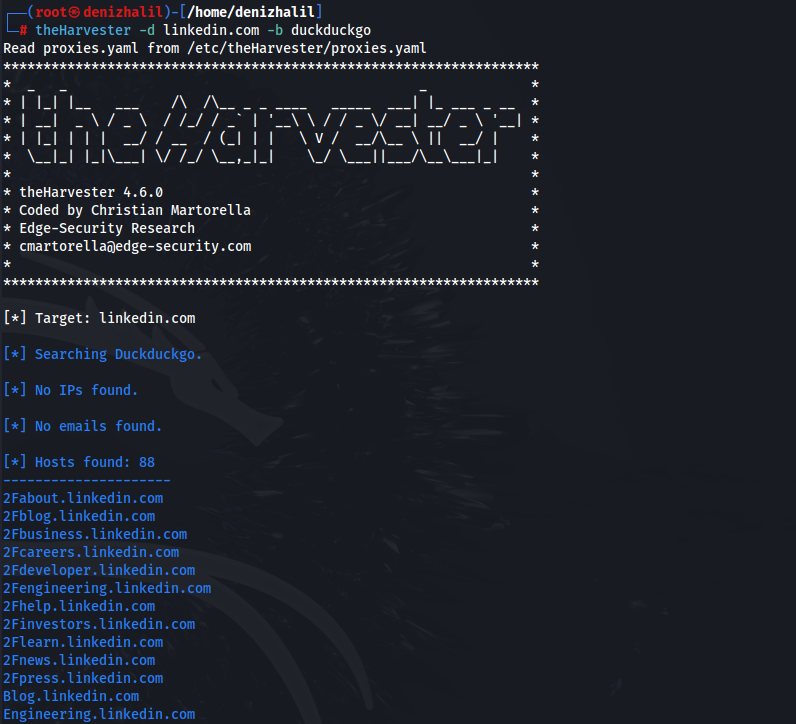
This command extracts information from Google related to “example.com,” useful for reconnaissance purposes.
4. Nmap
A versatile network scanning tool that can also perform DNS queries.
nmap -sL example.com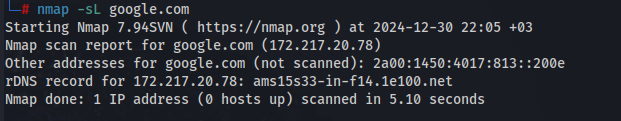
This command lists subdomains associated with “example.com,” aiding in identifying potential attack vectors.
5. dnsenum
A tool designed for comprehensive DNS enumeration tasks.
dnsenum example.com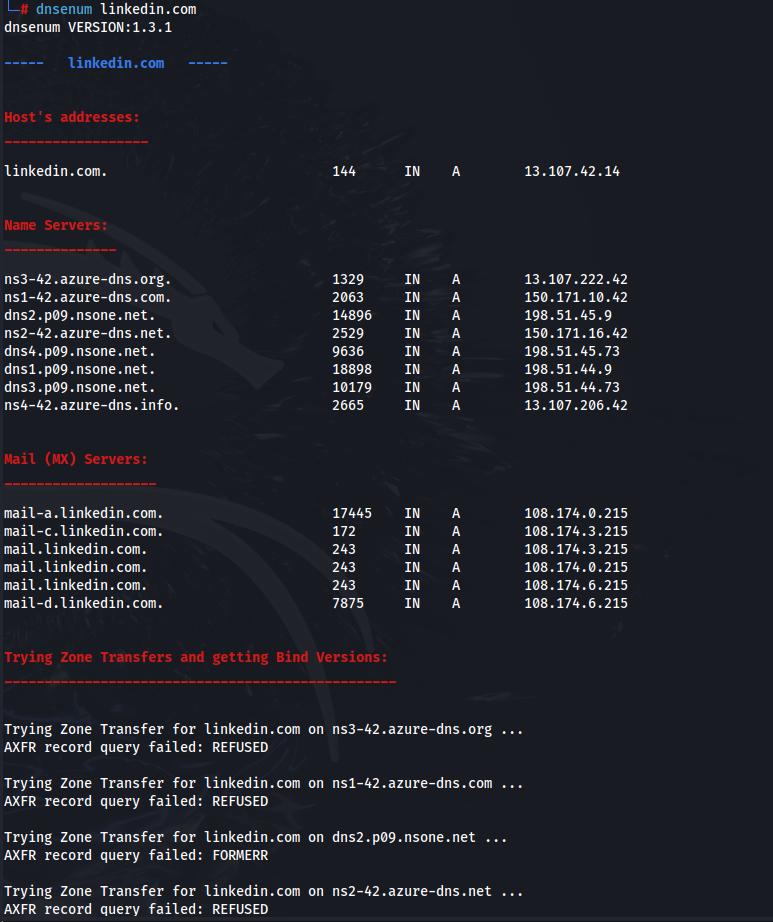
This command discovers subdomains and provides detailed information about “example.com.”
6. Sublist3r
A Python-based tool that leverages search engines to find subdomains.
sublist3r -d example.com -o sublist3r-results.txt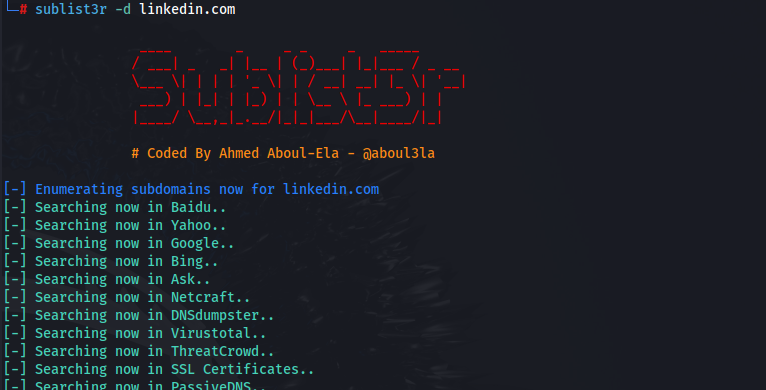
This command identifies subdomains for “example.com” and saves the results in a specified file.
7. Subbrute
A brute-force tool used for discovering subdomains.
subbrute example.com
This command performs a brute-force attack on “example.com” to uncover hidden subdomains.
Conclusion
DNS security is an integral aspect of maintaining a secure internet environment. As cyber threats continue to evolve, implementing effective security measures such as DNSSEC and utilizing various DNS security tools are essential steps in protecting both individual users and organizations. By understanding the importance of DNS security and leveraging available tools, stakeholders can enhance their defenses against potential attacks, ensuring a safer online experience for everyone. In summary, as we navigate an increasingly digital world, prioritizing DNS security will not only protect sensitive information but also foster trust and reliability in online interactions. Organizations must remain vigilant, continuously updating their security practices to adapt to new threats while ensuring their users’ safety and privacy in the digital landscape. The implementation of robust DNS security measures serves as a critical line of defense against cyber threats, safeguarding both individual users and business operations from potential harm.

