Introduction
As digital transformation accelerates and more aspects of our personal and professional lives move online, the threat landscape continues to evolve at an unprecedented pace. Ransomware attacks, in particular, have emerged as one of the most pervasive and damaging forms of cybercrime, targeting everyone from individuals and small businesses to large enterprises and critical infrastructure. In 2025, attackers are leveraging increasingly sophisticated tactics, such as artificial intelligence-driven social engineering, multi-layered extortion schemes, and targeted attacks on cloud and virtual environments. The diversity of targets and the complexity of attack methods mean that traditional security measures are often no longer sufficient. As a result, developing and maintaining robust, adaptive protection strategies has become essential for anyone seeking to safeguard their data and operations. This article provides a comprehensive overview of ransomware, examines the various types of ransomware attacks, outlines the critical steps to take if you become a victim, and details the most current and effective protection strategies for 2025.
Learning Objectives
- Understand the fundamentals of ransomware attacks and how they operate
- Identify different types of ransomware attacks
- Learn the steps to take if you fall victim to a ransomware attack
- Discover the latest and most effective protection strategies for 2025
What is a Ransomware Attack?
Ransomware is a highly disruptive type of malicious software (malware) designed to encrypt data on a victim’s computer system, rendering files, databases, and entire networks inaccessible until a ransom is paid—typically in cryptocurrency. Attackers often infiltrate systems using various tactics, with phishing emails containing malicious attachments or links being among the most common methods. Other entry points include exploiting unpatched software vulnerabilities, abusing insecure Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) connections, or leveraging drive-by downloads from compromised websites. Once inside the system, the ransomware spreads across the network, scanning for valuable files and escalating its privileges to maximize damage. The malware then encrypts critical data using advanced cryptographic techniques, effectively locking users out of their own information. In many modern attacks, cybercriminals not only encrypt data but also exfiltrate sensitive information, threatening to leak it publicly or sell it if their demands are not met.
The attack typically culminates in a ransom note displayed on the victim’s screen, demanding payment in exchange for a decryption key that may—or may not—restore access to the data. Ransomware attacks can have devastating consequences, including operational downtime, financial losses, reputational damage, and potential legal or regulatory repercussions. As attackers continually evolve their techniques to bypass security measures, ransomware remains one of the most formidable threats in the digital landscape today.
What Are the Types of Ransomware Attacks?
Ransomware attacks have evolved significantly in recent years, with cybercriminals deploying a variety of tactics to maximize their impact and profits. Understanding the different types of ransomware is crucial for developing effective defense strategies. Here are the main types of ransomware attacks seen in 2025:
- Encryption Ransomware (Crypto Ransomware): This is the most prevalent form of ransomware. It encrypts the victim’s files using strong cryptographic algorithms and demands payment—usually in cryptocurrency—for the decryption key. Without the key, recovering the data is nearly impossible, making this type especially devastating for organizations that lack reliable backups.
- Locker Ransomware: Unlike encryption ransomware, locker ransomware completely locks users out of their devices, preventing access to the operating system and applications. While the files themselves may not be encrypted, the inability to use the device can halt business operations until the ransom is paid. Locker ransomware often displays a ransom note on the locked screen, demanding payment for restoration of access.
- Doxware/Leakware: Also known as leakware, this type of ransomware not only encrypts or locks data but also threatens to publish or leak sensitive information if the ransom is not paid. This dual-threat approach increases the pressure on victims, especially organizations handling confidential customer data, intellectual property, or financial records. The risk of reputational damage and regulatory penalties makes doxware particularly dangerous.
- Scareware: Scareware uses psychological manipulation rather than direct encryption or system locking. It bombards users with fake warnings about security issues, urging them to purchase bogus software or pay a fee to “fix” non-existent problems. While less technically damaging than other ransomware types, scareware can still lead to financial loss and psychological stress.
- Mobile Ransomware: Targeting smartphones and tablets, mobile ransomware can lock devices or encrypt data, demanding payment to restore access. Some variants, like the Svpeng Trojan, specifically target banking apps and personal information on Android devices, making them a growing threat as mobile device usage increases.
- Triple Extortion Ransomware Attacks: This advanced attack method combines three layers of extortion. First, attackers encrypt the victim’s data. Second, they exfiltrate sensitive information and threaten to leak it. Third, they may launch additional attacks, such as Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks, or directly threaten customers, employees, or business partners, intensifying the pressure to pay multiple ransoms.
- Hypervisor Attacks: These attacks target virtualization platforms, such as VMware or Hyper-V, aiming to encrypt all virtual machines managed by the hypervisor simultaneously. This can cripple entire data centers or cloud environments, making recovery even more challenging.
Each type of ransomware poses unique challenges, and attackers are continually refining their techniques to bypass security defenses and increase their leverage over victims.
What Should I Do If I Am Attacked?
If you discover that your system has been targeted by ransomware, swift and deliberate action is crucial to minimize damage and begin the recovery process. Here is a more detailed guide on what to do:
- Isolate the System: The first and most critical step is to immediately disconnect the infected device from your network—this includes both wired and wireless connections. If possible, power down the device entirely to halt any ongoing encryption or data exfiltration. Also, disconnect or shut down other devices that were connected to the same network, especially those containing sensitive or valuable information, to prevent the ransomware from spreading further.
- Notify Authorities: Inform your internal IT or security team as soon as possible. If you are part of an organization, follow established incident response protocols. In cases where sensitive data is involved or if required by law, notify relevant cybercrime authorities or regulatory bodies. Reporting the incident can also help law enforcement track and combat ransomware operations.
- Check Backups: Assess the integrity of your backups. Ensure they are recent, clean, and have not been compromised by the ransomware. Do not reconnect backup drives or cloud storage to the infected system before verifying their safety. If your backups are unaffected, you can use them to restore your data after the ransomware has been removed from your environment.
- Do Not Pay the Ransom: Experts strongly advise against paying the ransom. There is no guarantee that paying will result in the return of your data, and it encourages attackers to continue their activities. Additionally, paying may make your organization a repeat target. Focus instead on recovering from clean backups and strengthening your security posture.
- Analyze the Incident: After containment, work with your IT or a specialized incident response team to analyze the attack. Determine how the ransomware entered your system, what data or systems were affected, and whether any sensitive information was exfiltrated. Collect logs, system images, and evidence for forensic analysis, which can help prevent future incidents and improve your defenses.
- Change Passwords and Secure Accounts: Some ransomware strains steal credentials. As a precaution, change passwords for your most important accounts, such as email, cloud storage, and banking, especially if you suspect they may have been compromised.
- Report and Learn: Report the incident to appropriate authorities and, if applicable, to affected stakeholders. Use the lessons learned from the attack to update your security policies, improve user training, and implement stronger preventive measures for the future.
Taking these steps methodically will help you respond effectively to a ransomware attack, limit its impact, and reduce the likelihood of future incidents.
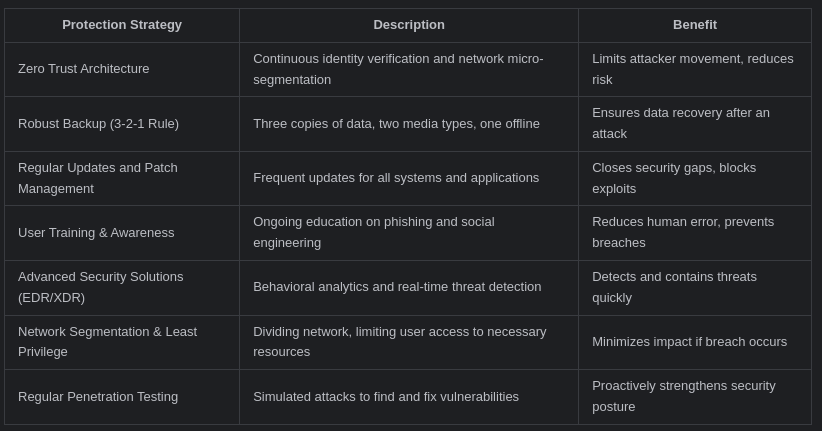
Effective Ransomware Protection Strategies for 2025
The evolving threat landscape of 2025 demands comprehensive and adaptive strategies to counter ransomware attacks. Organizations must stay ahead of cybercriminals by implementing a multi-layered defense approach. Below is an expanded guide to the most effective protection Protection strategies for this year:
- Adopt Zero Trust Architecture: Zero Trust is a security model that assumes no user or device—inside or outside the network—should be trusted by default. It requires strict identity verification for every person and device attempting to access resources. Micro-segmentation is a key component, dividing the network into smaller, isolated zones to contain threats and prevent lateral movement by attackers. Continuous monitoring and least privilege access further reduce the risk of ransomware spreading if an initial breach occurs.
- Robust Backup Strategies: Regular, secure backups are your last line of defense. The 3-2-1 backup rule is foundational: maintain three copies of your data, store them on two different types of media, and keep one copy offline or immutable. This ensures that even if ransomware attacks encrypts your primary data, you can restore from a clean backup. Consider upgrading to the 3-2-1-1-0 strategy for added protection, where one backup is immutable and another is air-gapped.
- Keep Systems and Software Updated: Cybercriminals exploit unpatched vulnerabilities to infiltrate systems. Regularly update all operating systems, applications, and firmware to close security gaps. Enable automatic updates where possible and monitor for new patches from vendors. This reduces the attack surface and makes it harder for ransomware to gain a foothold.
- User Training and Awareness: Human error remains a leading cause of ransomware Protection infections. Provide ongoing training to educate employees about phishing, social engineering, and safe online practices. Simulated phishing exercises can help reinforce awareness and improve vigilance. Well-informed users are less likely to fall for malicious emails or links.
- Advanced Security Solutions: Traditional antivirus software is no longer enough. Deploy endpoint detection and response (EDR) or extended detection and response (XDR) solutions that use behavioral analytics, AI, and machine learning to detect and respond to ransomware in real time. These tools can identify suspicious activities, automate investigations, and isolate infected devices before significant damage occurs.
- Network Segmentation and Least Privilege: Divide your network into smaller, isolated segments to limit the spread of ransomware if a breach occurs. Restrict user access to the minimum necessary for their roles, and regularly audit permissions. This containment strategy reduces the impact of an attack and protects critical systems from widespread compromise.
- Regular Penetration Testing: Proactively test your defenses by simulating ransomware attacks and other cyber threats. Penetration testing helps identify vulnerabilities before attackers do, allowing you to patch weaknesses and improve your security posture. Regular testing ensures your protection strategies remain effective against evolving threats.
By integrating these strategies, organizations can build a resilient security framework that minimizes the risk of ransomware attacks and ensures rapid recovery if an incident occurs.
Conclusion
As we progress through 2025, ransomware attacks have reached unprecedented levels of sophistication, leveraging artificial intelligence, multi-layered extortion techniques, and increasingly targeted attack vectors. Cybercriminals are no longer content with simply encrypting data—they now threaten to leak sensitive information, disrupt services, and even target third parties, amplifying the pressure on victims. This evolving threat landscape makes it clear that relying solely on traditional security measures is no longer sufficient. Effective protection against ransomware demands a comprehensive, multi-layered approach that combines advanced technological solutions with robust user education and proactive security policies. Organizations must implement strategies such as Zero Trust architecture, rigorous backup protocols, continuous system updates, and advanced threat detection tools. Equally important is fostering a culture of security awareness, where employees are trained to recognize and respond to phishing attempts and other common attack vectors.
By integrating these elements, both organizations and individuals can build resilient defenses that significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to ransomware. Staying informed about the latest threats, regularly testing and updating security measures, and maintaining vigilance will be key to navigating the cybersecurity challenges of 2025 and beyond. Ultimately, a proactive and adaptive security posture is the best defense against the ever-changing tactics of ransomware Protection attackers.
Get in Touch for Business Offers, Problem Solving, and Professional Proposals
If you are seeking expert solutions for your cybersecurity challenges, require a tailored business offer, or need professional consulting, we invite you to contact us. Our team delivers a comprehensive range of cybersecurity services—including penetration testing, network security, application security, and social engineering assessments—designed to meet the unique needs of your organization[1].
For business inquiries, partnership opportunities, or to discuss your specific requirements, please reach out:
- Cyber Security Services: Visit our services page for detailed information: denizhalil.com/cybersecurity-services-solutions/
- Contact Information: Find all contact details at: denizhalil.com/contact-informations/
- Email: halildeniz@denizhalil.com
Let us help you strengthen your cyber defenses and provide

