Introduction
The Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized various aspects of our daily lives, ranging from smart home appliances to wearable devices, industrial automation systems, and health monitoring tools. However, the increasing use of these devices has also raised significant security concerns. IoT devices are often equipped with weak security standards, making them attractive targets for cyber attackers. This article will explore the importance of IoT security, its fundamental security components, the types of attacks IoT devices are most vulnerable to, and how to address security requirements effectively.
Learning Objectives
- Understand the definition and importance of IoT security.
- Learn about the fundamental security components of IoT devices.
- Identify the types of attacks that IoT devices are most vulnerable to.
- Explore how to meet IoT security requirements.
- Discover ways to identify vulnerable IoT devices using tools like Shodan.
What is IoT Security?
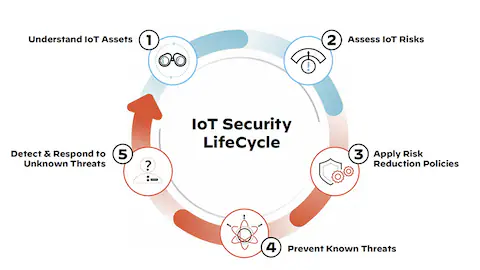
IoT security refers to the strategies and technologies designed to protect connected devices and networks within the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem. As IoT devices grow in number across various sectors—from smart home appliances to industrial systems—the need for robust security measures becomes critical. These measures aim to defend against cyber threats, particularly targeting devices with weak security standards. IoT security encompasses both the physical protection of individual devices and the broader network security that connects them. A vulnerability in one device can compromise the entire system, making a multi-layered security strategy essential. This includes strong authentication, data encryption, and regular firmware updates tailored to specific use cases. With predictions of over 30 billion connected devices by 2030, the potential attack surface for cyber threats is expanding rapidly. Therefore, effective IoT security is vital for safeguarding assets and ensuring operational integrity in an increasingly interconnected world.
Fundamental Security Components of IoT Devices
To ensure the security of IoT devices, several fundamental components must be considered:
- Strong Authentication: The authentication mechanisms for devices should be robust; weak passwords must be avoided. Users should be encouraged to change default passwords and utilize multi-factor authentication (MFA) where possible. This adds an additional layer of security by requiring more than just a password for access.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting data transmitted between devices is critical for maintaining data privacy. Encryption methods should be applied during both data transmission and storage to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access. End-to-end encryption ensures that data remains secure throughout its journey from source to destination.
- Updates and Patching: Regular software updates for devices are essential to close known vulnerabilities. Manufacturers should ensure that updates can be easily communicated to users, and automated update mechanisms can help keep devices secure without requiring user intervention. This proactive approach is vital in addressing newly discovered threats.
- Network Security: The networks that IoT devices connect to must be secured; measures should be taken against unauthorized access. Using a secure Wi-Fi network, implementing firewalls, and regularly monitoring all connected devices is crucial for detecting suspicious activity and preventing breaches.
- Physical Security: Protecting devices from physical tampering is also important, especially for IoT devices used in critical infrastructure. Measures such as tamper-proof hardware, surveillance systems, and secure installation practices can help mitigate risks associated with physical attacks.
- Device Management: Effective device management is essential for maintaining the security of IoT devices throughout their lifecycle. This includes establishing clear policies for device onboarding, monitoring, and retirement. Organizations should implement centralized management systems that allow for real-time monitoring of device health and security status, enabling quick responses to any identified vulnerabilities or anomalies.
By addressing these fundamental components, organizations can significantly enhance the security posture of their IoT deployments and mitigate the risks associated with the increasing number of connected devices.
Types of Attacks That IoT Devices Are Most Vulnerable To
IoT devices are particularly vulnerable to the following types of attacks:
- Unauthorized Access: Weak authentication mechanisms can allow attackers to gain unauthorized access to devices. The failure to change default passwords exacerbates this issue, making it easier for malicious actors to exploit vulnerabilities.
- Data Theft: The risk of data theft is significant during the collection and processing of personal data. Attackers can intercept transmitted data, gaining access to sensitive information such as personal identification, financial details, and private communications.
- DDoS Attacks: Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks target multiple devices simultaneously, overwhelming network resources and disrupting functionality. These attacks are often executed using botnets comprised of compromised IoT devices, which can be manipulated to flood a target with traffic.
- Firmware Attacks: Vulnerabilities in device firmware can be exploited by malicious actors. When firmware updates are not applied regularly, the risk of exploitation increases, allowing attackers to take control of devices or install malicious software.
- Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks: This type of attack involves intercepting communications between two parties, threatening data integrity and confidentiality. Attackers can eavesdrop on sensitive information or manipulate data being transmitted between devices.
- Device Hijacking: Attackers may compromise IoT devices to take control of their functions, using them as entry points for further attacks or to disrupt operations. This can lead to unauthorized control over critical systems, potentially resulting in severe consequences for both individuals and organizations.
These vulnerabilities highlight the urgent need for robust security measures in IoT deployments. As the number of connected devices continues to grow, so does the potential attack surface for cyber threats, making it essential for organizations and users to implement comprehensive security strategies that address these risks effectively.
Our Network Security Services: Comprehensive Protection for Modern Business Networks
How To Address IoT Security Requirements?
To effectively meet IoT security requirements, organizations should implement a comprehensive strategy that encompasses several key steps:
- Implementation of Security Protocols: Employing strong encryption methods, such as Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), is essential for securing communications between devices. Additionally, protocols like TLS (Transport Layer Security) and SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) should be utilized to ensure that data transmitted over networks remains confidential and tamper-proof. These protocols help protect sensitive information from interception and unauthorized access during transmission.
- Education and Awareness: Providing cybersecurity training for users and developers is crucial in fostering a culture of security awareness. Users should be educated about the risks associated with IoT devices, including the importance of changing default credentials and recognizing phishing attempts. Regular training sessions can help keep both users and developers informed about the latest threats and best practices, significantly reducing vulnerabilities within the system.
- Centralized Management Systems: Establishing a centralized management system for device identity, configuration, and software updates allows for better monitoring and management of all connected devices. This system should facilitate real-time visibility into the security status of each device, enabling organizations to quickly identify and respond to potential threats or anomalies. Centralized management also streamlines the process of applying updates and patches across multiple devices.
- Security Testing and Audits: Conducting regular penetration testing and security audits is vital for identifying weaknesses in the system before they can be exploited by attackers. These assessments should include vulnerability scanning, risk assessments, and compliance checks to ensure that all devices adhere to established security standards. By proactively identifying potential vulnerabilities, organizations can implement necessary fixes before they are targeted by cybercriminals.
- Incident Response Plans: Developing comprehensive incident response plans enables organizations to act swiftly in the event of a cyber attack. These plans should outline clear procedures for identifying, containing, eradicating, and recovering from security incidents. Regularly testing these plans through simulations can help ensure that all team members are familiar with their roles during an actual incident, minimizing response time and potential damage.
- Continuous Monitoring and Threat Intelligence: Implementing continuous monitoring solutions allows organizations to track the behavior of IoT devices in real-time. This includes monitoring network traffic for unusual patterns that may indicate a security breach or an attempted attack. Coupled with threat intelligence services, organizations can stay informed about emerging threats specific to IoT environments, enabling them to adapt their security measures proactively.
By addressing these key areas, organizations can significantly enhance their IoT security posture and mitigate the risks associated with an increasingly interconnected world. A proactive approach that combines robust technical measures with ongoing education and incident preparedness will help safeguard against the evolving landscape of cyber threats targeting IoT devices.
Conclusion
IoT security is becoming increasingly important in today’s digital landscape, where the rapid growth of connected devices is transforming how we interact with technology. As the number and variety of IoT devices expand—from smart home appliances to industrial sensors—the potential attack surface for cyber threats also increases. This evolution brings numerous security risks that must be effectively addressed by both individuals and organizations to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of data. Implementing strong authentication mechanisms is essential for protecting IoT devices, as it ensures that only authorized users can access them. Additionally, employing robust data encryption methods is critical for safeguarding sensitive information during transmission and storage. Regular updates and patches are equally vital; many cyber attacks exploit known vulnerabilities that could have been mitigated through timely software updates.
Enhancing user education and awareness plays a crucial role in an effective security strategy. Training users on recognizing phishing attempts, changing default passwords, and understanding the importance of updates can significantly reduce human-related vulnerabilities. As more connected devices emerge, ongoing efforts in IoT security will remain essential. The landscape of cyber threats is continually evolving, making it imperative for organizations to adopt a proactive approach that includes continuous monitoring and incident response planning. In summary, addressing IoT security challenges requires a multi-faceted approach that combines technical measures with user education. By prioritizing IoT security as a core component of their operational strategies, organizations can better protect their assets against the growing array of cyber threats, ensuring a safer and more secure interconnected world.

How can we find IoT devices?
shodan or censys can help you very well