Introduction
In today’s digital age, creating a strong password is a critical aspect of securing personal and organizational information. Weak passwords are easily cracked by attackers, putting sensitive data at risk. This article explores a Python-based tool designed to evaluate password strength by analyzing key factors like length, character variety, and complexity. Using a Password Strength Checker in Python with color-coded outputs for clarity, this tool serves as a straightforward, user-friendly way to assess password security.
Learning Objectives
By the end of this article, readers will be able to:
- Understand essential elements that make a password strong.
- Identify weaknesses in passwords by analyzing length and character diversity.
- Build a simple Python tool to assess password strength.
- Gain experience using
coloramafor colored output in Python.
Purpose of This Project
The primary goal of this project is to create a Python tool that helps users evaluate the strength of a password quickly and effectively. By focusing on parameters like password length and character types (uppercase, lowercase, numbers, special characters), we can estimate how resistant a password might be against brute-force or dictionary attacks. This tool is especially useful for cybersecurity enthusiasts, developers, and anyone who wants to improve password practices.
Read: Assessing Password Strength with Machine Learning in Python
Let’s Start Coding
We’ll build this project step-by-step, starting with defining the PasswordStrengthTester class. This class includes methods for calculating password strength and displaying the result with colored feedback using the colorama library.
Step 1: Setting Up and Importing Libraries
To begin, we import the necessary modules for our project. The re module (for regular expressions) is used to check for different types of characters in the password, such as lowercase letters, uppercase letters, digits, and special characters. This helps us determine the password’s complexity.
import re
from colorama import Fore, Style, init
init(autoreset=True)The colorama library is used to add color to the output, making it visually engaging and easier to interpret. The Fore class in colorama allows us to choose specific colors, and Style provides styling options. We call init(autoreset=True) to ensure that each line resets to the default terminal style after each print, which prevents colors from unintentionally carrying over to other parts of the terminal output.
Step 2: Building the PasswordStrengthTester Class
The PasswordStrengthTester class is the core of our password evaluation tool. The __init__ method initializes the class with two attributes:
password: The password provided by the user.strength_score: A score to measure the password’s strength, initialized at 0
class PasswordStrengthTester:
def __init__(self, password):
self.password = password
self.strength_score = 0Each password attribute (length and character type) will add points to this score, which is later used to determine the password’s strength level.
Step 3: Writing the calculate_strength Method
In the calculate_strength method, we assess the password using a set of predefined criteria. For each criterion met, we increment the strength_score by 1. Here’s a breakdown of the tests:
- Length Test: A minimum length of 8 characters adds 1 point to the score, as it is generally considered a baseline for password length. An additional point is added if the length is 12 or more characters, which further increases security.
- Character Diversity Tests:
- Lowercase Letters: If the password contains lowercase letters (
[a-z]), it gains a point. - Uppercase Letters: If the password contains uppercase letters (
[A-Z]), it gains another point. - Digits: Including numbers (
[0-9]) contributes to complexity, so this adds a point as well. - Special Characters: Using special characters (e.g.,
@,#,$,%, etc.) further strengthens the password, so it adds another point.
- Lowercase Letters: If the password contains lowercase letters (
def calculate_strength(self):
self.strength_score = 0
# Length test
if len(self.password) >= 8:
self.strength_score += 1
if len(self.password) >= 12:
self.strength_score += 1
# Character diversity tests
if re.search("[a-z]", self.password): # Lowercase letter
self.strength_score += 1
if re.search("[A-Z]", self.password): # Uppercase letter
self.strength_score += 1
if re.search("[0-9]", self.password): # Digit
self.strength_score += 1
if re.search("[@#$%^&*()_+=]", self.password): # Special character
self.strength_score += 1By combining these checks, the calculate_strength method gives a clear view of the password’s strength, helping users understand how diverse and secure their password is.
Step 4: Writing the display_strength Method
The display_strength method interprets the score and provides a color-coded output that helps users understand the password’s security level at a glance:
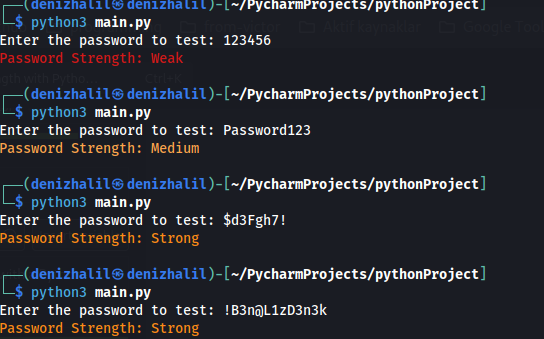
- Weak (Red): For passwords with a score of 2 or below, indicating insufficient strength and high vulnerability.
- Medium (Yellow): A score of 3-4, indicating moderate security but still lacking in certain areas.
- Strong (Light Yellow): A score of 5-6, where the password meets most security criteria.
- Very Strong (Green): A score above 6, indicating an excellent password that is resistant to common cracking techniques.
def display_strength(self):
if self.strength_score <= 2:
print(Fore.RED + "Password Strength: Weak")
elif self.strength_score <= 4:
print(Fore.YELLOW + "Password Strength: Medium")
elif self.strength_score <= 6:
print(Fore.LIGHTYELLOW_EX + "Password Strength: Strong")
else:
print(Fore.GREEN + "Password Strength: Very Strong")Each level provides visual feedback through colors to quickly indicate security levels, making it user-friendly and easily interpretable.
Read: Improving Password Security with Machine Learning
Step 5: Running the Program
Finally, we prompt the user to enter a password through input() and then create an instance of the PasswordStrengthTester class. By calling the run() method on this instance, the tool evaluates the password’s strength and displays the result.
if __name__ == "__main__":
password = input("Enter the password to test: ")
tester = PasswordStrengthTester(password)
tester.run()This final step makes the tool interactive and straightforward to use, requiring minimal input from the user and providing immediate feedback.
Conclusion
With this simple yet powerful Python tool, users can quickly evaluate the strength of their passwords. This project reinforces the importance of secure password practices by demonstrating how easy it is to identify weak passwords. As a next step, you can expand this tool to provide suggestions for improving weak passwords or integrate it into a larger security application. This exercise serves as a fundamental but impactful example of how Python can enhance cybersecurity practices.
Mastering Advanced Python from Scratch to Advanced
Unlock the full potential of Python with this comprehensive guide, spanning 227 pages and 50 chapters. From advanced techniques like metaprogramming.
-5% 25 on buymeacoffee


In the regex pattern for special characters, why did you choose to include only a specific subset of characters? Are other characters less common or secure?
The specific subset of special characters was chosen to cover the most commonly used symbols in passwords. Including more characters can enhance security but may require additional handling if they have special meanings in regex. You can expand the character set by modifying the regex pattern to include more symbols like re.search(“[@#$%^&*()_+=|\{\}’:;,.<>\[\]\\\”~-!]”, self.password)`.
Longer passwords often provide greater security. Consider explaining more about entropy and how password length exponentially increases the difficulty of brute-force attacks.
How does the init(autoreset=True) function from colorama affect the output in different terminals?
init(autoreset=True) in colorama ensures that every print statement automatically returns to the default color and style after execution. This prevents the color settings from one print statement from affecting the text of subsequent prints, which can be particularly useful in complex console applications where color consistency is crucial.
Could this tool be adapted to provide real-time feedback as a user types a password in a form field?
Absolutely, to provide real-time feedback, you could use JavaScript for client-side validation based on the logic defined in your Python script. However, you’d need to convert the logic into JavaScript or make AJAX calls to a Python script running on the server.