Introduction
Reverse engineering is a systematic analysis process aimed at understanding the operational principles of an existing product or system. This process can be applied to software, hardware, or mechanical systems and plays a critical role in areas such as security analysis, product development, and the creation of innovative solutions. By enabling a deeper understanding of complex systems, reverse engineering also lays the groundwork for new designs and improvements. With the rapid advancement of technology today, the applications of reverse engineering are on the rise. This article will discuss what reverse engineering is, its areas of application, and popular tools used in the field.
Learning Objectives
By the end of this article, readers will be able to:
- Understand the definition and significance of reverse engineering,
- Explore various application areas of reverse engineering,
- Identify popular reverse engineering tools,
- Grasp the role of reverse engineering in contemporary settings,
- Gain insight into how reverse engineering processes operate.
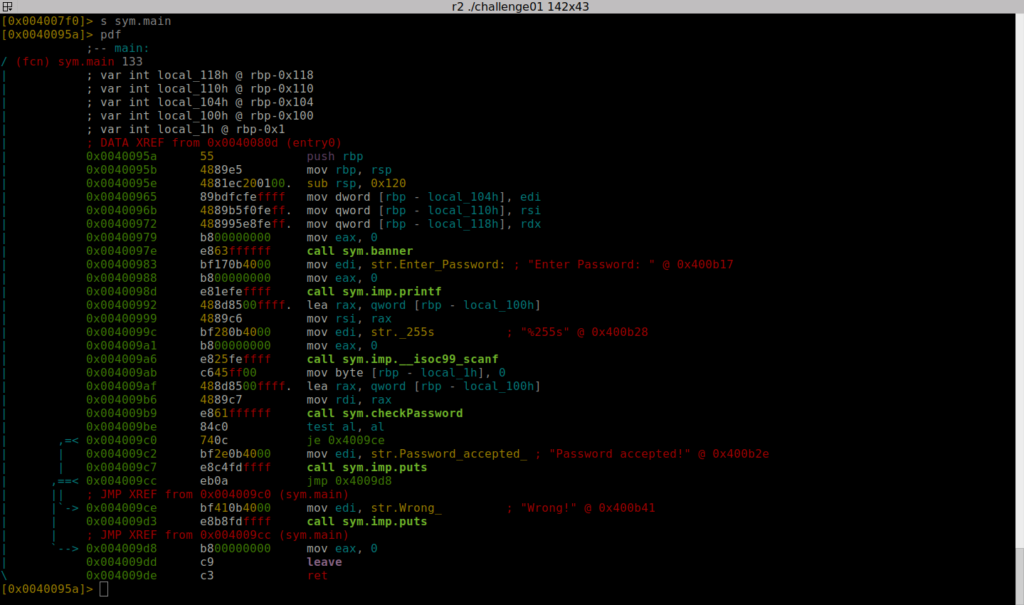
What is Reverse Engineering?
Reverse engineering is a systematic process that involves deconstructing a product or system to understand its design, functionality, and operational logic. This method is widely used across various industries, including software, electronics, automotive, and mechanical engineering. The primary objective of reverse engineering is to extract valuable insights from existing products, which can then be used to improve designs, create compatible versions, or develop entirely new innovations. The process typically consists of several key steps:
- Analysis: The first step involves a thorough examination of the current state of the product or system. This phase includes gathering information about the structure, components, and operation of the product. Analysts may use various techniques such as visual inspections, functional testing, and even user feedback to collect comprehensive data. Understanding how the product works in practice is crucial for identifying its strengths and weaknesses.
- Documentation: Once sufficient information is gathered, it is documented using graphs, diagrams, or written reports. This step creates an important reference source for future analyses and serves as a foundation for further development. Effective documentation ensures that insights gained from reverse engineering can be communicated clearly among team members and stakeholders.
- Reconstruction: Using the data collected during the analysis phase, engineers can design a new version of the product or system. This phase may involve improving existing products by incorporating new technologies or redesigning components to enhance performance. Alternatively, it may lead to the creation of entirely new designs based on the insights gained from the original product. Reconstruction not only aims to replicate functionality but also seeks to innovate by addressing identified shortcomings.
Reverse engineering is particularly prevalent in software development and security testing. In these fields, it plays a crucial role in analyzing malicious software (malware) and identifying security vulnerabilities within applications. By understanding how malware operates, security professionals can develop effective countermeasures and enhance overall system security.
Mastering Linux Networking and Security
As you progress through this book, you’ll gain the skills necessary to not only manage networks but also protect them from the ever-evolving threats that exist in today’s digital landscape.
-5% 18 on buymeacoffeeApplications of Reverse Engineering
Reverse engineering can be applied in many different areas. Here are some significant application domains:
- Software Security: Techniques from reverse engineering are employed to identify vulnerabilities in software. By analyzing the effects of malicious software, defense strategies can be developed. Additionally, these methods are critical for understanding software weaknesses.
- Product Development: It assists in examining existing product designs to help develop better versions. By analyzing competitor products’ features, innovative solutions can be generated.
- Competitive Analysis: It can be used to analyze competitors’ products and formulate market strategies. This allows businesses to gather necessary information for enhancing their own products.
- Debugging: It plays an important role in detecting and correcting software bugs. Developers can utilize reverse engineering techniques to make their software more stable.
- Education and Research: Reverse engineering serves as a valuable learning tool for engineering students and researchers. It provides practical opportunities to understand how complex systems work.
Popular Reverse Engineering Tools
There are various tools used in the reverse engineering process. Here are eight popular reverse engineering tools:
- IDA Pro: An advanced disassembler that offers interactive analysis capabilities. Users can rename functions and variables for better understanding, modify data representations, and create flowcharts. It is particularly favored for analyzing complex software.
- Ghidra: Developed by NSA, this open-source tool stands out with its multi-platform support. Ghidra helps users analyze binary files and features a powerful decompiler capability. Its user-friendly interface makes it accessible for both beginners and experienced users.
- OllyDbg: A popular debugger for Windows-based software. Its user-friendly interface simplifies debugging processes. Real-time monitoring features allow developers to make instantaneous changes to code.
- Radare2: An open-source reverse engineering framework that supports numerous architectures but has a steeper learning curve. Its command-line-based structure provides advanced users with a wide range of features.
- Binary Ninja: This tool functions as both a disassembler and decompiler, allowing users to convert code into C language format. It also offers API support for automated analysis, enabling developers to create their own plugins.
- Frida: Used for dynamic analysis, this tool allows code injection into running processes. It is frequently employed in mobile application research for conducting security tests on Android and iOS platforms.
- Wireshark: A tool used for monitoring network traffic that analyzes data sent and received by applications over the internet. It provides crucial insights through protocol analysis regarding network security.
- PEiD: A tool used for packer detection that conducts entropy analysis to determine whether an application has been packed or not. It is beneficial for analysts looking to understand whether software is protected against reverse engineering.
Conclusion
Reverse engineering holds critical importance in various fields such as software security, product development, and competitive analysis today. The diverse range of tools used in this process aids analysts and developers in gaining a better understanding of existing systems while facilitating improvements. The advantages provided by reverse engineering make it possible to generate innovative solutions at both individual and corporate levels. In today’s technology-driven world, learning and applying the fundamentals of reverse engineering emerges as an essential skill; thus, it is crucial for software developers and security professionals to continuously update their knowledge and skills in this area. Furthermore, reverse engineering contributes not only to understanding current systems but also to shaping future technologies; therefore, ongoing efforts in this field are of great significance.



You’re in reality a good webmaster. This website loading pace is incredible.
It sort of feels that you’re doing any distinctive trick.
Do you plan to make a detailed explanation for these types of tools?
you can just search on the google or youtube and learn them
if i have free time of course